EUginius, the European GMO Reference Database
EUginius (EUropean GMO INItiative
for a Unified Database System) is an initiative of BVL - the Federal Office of
Consumer Protection and Food Safety (Berlin, DE) and Wageningen Food Safety
Research (Wageningen, NL) to support competent authorities and private users
who seek accurate information on GMOs. EUginius is supported by the Austrian
Agency for Health and Food Safety Ltd. (AGES) (www.ages.at), the Plant Breeding and Acclimatization
Institute (IHAR) (www.ihar.edu.pl) and the Experimental Zooprophylactic Institute of
Lazio and Tuscany (IZSLT) (www.izslt.it).
EUginius provides
accurate information of major and relevant issues regarding the presence, detection
and identification of GMOs with a focus on the situation in the European Union
as well as world-wide coverage.
Access to the
EUginius.eu database is open for use by anyone and is intended to support competent authorities as
well as private users.
For unrestricted
access to EUginius you must have an account with proper authorisations. For the
terms and conditions regarding authorised use consult 6.1 Terms of use. Access can be
granted by BVL staff and can be requested via databasemanager@euginius.eu.
EUginius has 3 authorised access levels.
1.2.2.1
Read-only
Read Only grants
additional access to confidential information as well as modules that are under
construction. This includes:
·
BLAST Module
·
Safety Literature Module
1.2.2.2
Data entry
Data entry users have access to all levels
which Read Only covers, plus access to the Data Entry module. They are able to
enter new data or initiate modification or deletion of existing entries. This
is part of EUginius’ 6-eyes data entry system.
1.2.2.3
Expert
Expert users have access to all levels
which Read Only covers, plus access to the Data Entry module. They are able to validate
new data, modification and deletion of existing entries. This is part of EUginius’
6-eyes data entry system.
1.2.2.4
Administrator
The administrator
has access to all modules, and can edit these. For any help, information or
feedback contact an administrator via databasemanager@euginius.eu.
General
For general questions
about EUginius you can contact Wageningen Food Safety Research via email euginius.wfsr@wur.nl or at
+31(0)317480256 or the BVL via email 405@bvl.bund.de
or at +49(0)301844440503.
Input
or Feedback
For any input find
the hyperlinks on the homepage or consult 5.1 Input and Feedback.
Database
In case of questions about
the database, contact database@euginius.eu
Website
In case of questions about
the website, contact webmaster@euginius.eu
Relevant
Institutions
EUginius is a collaborative effort between BVL - the Federal Office of Consumer
Protection and Food Safety (Berlin, DE) and Wageningen Food Safety Research (WFSR).
|

|

|
|
Wageningen Food Safety Research
Department Statutory Tasks
|
Federal Office of Consumer Protection and
Food Safety
Department Genetic Engineering
|
|
T +31 (0)317 480256
euginius.wfsr@wur.nl
www.wur.eu/wfsr
|
T +49-(0)3018-444-40000
gentechnik@bvl.bund.de
www.bvl.bund.de
|
|
Visiting address:
Akkermaalsbos 2
Building no. 123
6708 WB WAGENINGEN
The Netherlands
|
Visiting address:
Gerichtstraße 49
13347 BERLIN
Germany
|
|
Mail address:
PO Box 230
6700 AE WAGENINGEN
The Netherlands
|
Mail address:
PO Box 11 02 60
10832 BERLIN
Germany
|
1.4 Organisation
of the Manual
This manual offers
internal hyperlinks that allow you to travel through it more efficiently. These
are written as 1.4 Organisation of the Manual
(italic and underlined). They will take you to the place in the manual which
the text references. The hyperlinks in blue font lead you to the EUginius
website.
The manual is
divided into 6 major sections:
|
1.0
|
General Information
|
Basic information about EUginius, such as functions performed and
a description of the program.
|
|
2.0
|
Getting Started
|
General walk-through of the system including getting into EUginius.
|
|
3.0
|
Using the System
|
Detailed description of the system’s
functions from start to finish.
|
|
4.0
|
Workflow
|
An example for using the analysis tool, finding detailed
information and designing your own screening.
|
|
5.0
|
Input and Feedback
|
The standard procedure for
system malfunction or improvement opportunities.
|
|
6.0
|
Terms and Condition of Use
|
Additional data to assist you
when working in EUginius.
|
|
GMO
|
Genetically Modified Organism
|
|
Event
|
Used when describing one particular GMO derived from a
transformation process as well as genome edited organisms (GE-GMO)
|
|
UID
|
Unique Identifier which is
given to events for standardisation between databases
|
|
Stack
|
A traditional crossing of two GMO
events to create a plant that exhibits both features
|
|
Element
|
A DNA sequence that can be
inserted into an organism where it will perform a specific function. In case
of GE-GMO, DNA sequence which has been modified.
|
|
Coding Sequence
|
An element that consists of DNA coding for a protein
|
|
Promoter
|
An element that initiates transcription of a particular coding
sequence
|
|
Terminator
|
An element that marks the end of a particular coding sequence,
ending transcription
|
|
Construct
|
Two or more genetic elements aligned next to each other
|
|
BLAST
|
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
|
|
Authorisation
|
Official permission for the use of specific GMOs
|
|
Food
|
Product for human consumption
|
|
Feed
|
Product for animal consumption
|
|
Cultivation
|
Growing the GMO as crop
|
|
Transformation
|
Genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and
incorporation of exogenous genetic material
|
|
Insert
|
DNA sequence that has
integrated into the genome of a species during transformation
|
|
Vector
|
DNA fragment that was
used in the process of transformation
|
|
Free-text search
|
A search which allows
for manual entry of any word/phrase you choose
|
|
Query-building search
|
A search which allows for
multiple keywords which can be selected from a drop-down list
|
General
|
BLAST
|
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
|
|
GE
|
Genome Edited
|
|
GMO
|
Genetically Modified Organism
|
|
PCR
|
Polymerase Chain Reaction
|
|
UID
|
Unique IDentifier
|
Genetic Elements
|
CS
|
Coding
Sequence
|
|
E
|
Enhancer
|
|
I
|
Intron
|
|
L
|
Leader
|
|
O
|
Other
sequences
|
|
P
|
Promoter
|
|
R
|
Regulatory
element
|
|
T
|
Terminator
|
|
TP
|
Transit
Peptide
|
|
V
|
Vector
fragment
|
Detection Methods
|
QL-
|
Qualitative (PCR method)
|
|
QT-
|
Quantitative
(PCR method)
|
|
-CON-
|
Construct-specific
method
|
|
-ELE-
|
Element-specific
method
|
|
-EVE-
|
Event-specific
method
|
|
-TAX-
|
Taxon-specific
method
|
Institutions
|
EUginius
|
EUropean GMO INItiative for a Unified database System
|
|
BCH
|
Biosafety Clearing-House
|
|
NCBI
|
National Center for Biotechnology Information
|
|
ISO
|
International Organization for Standardization
|
|
CEN
|
European Committee for Standardization (Comité
Européen de Normalisation)
|
|
EURL
|
European Union Reference Laboratory
|
2.0
Getting Started
Public (euginius.eu)
Access to
EUginius.eu is public and does not require an account. Terms of use can be
found in EUginius’ footer under 6.1 Terms of Use. This
public version has the following modules:
·
Home
·
GMO
·
Detection
·
Analysis
·
Authorisation
·
Search
·
Help
Private
An account is required to access the private version of EUginius.
In addition to the
publically available modules, the private version offers the following modules:
·
BLAST
·
Safety Literature
·
Data Entry

Figure 1 - EUginius menu (public version)
Upon launching the
system, you are presented with the homepage with a blue menu bar (Figure 1). By clicking the labelled tabs, you can move to the following sections:
·
GMO
·
Detection
·
Analysis
·
Authorisation
·
Search
·
Help
Below the labelled tabs there are three central
sections and a toolbar. At the very bottom of the page are hyperlinks to the
Disclaimer, Terms of use, Contact information.
2.2.1.1
Homepage toolbar (left)
The toolbar is comprised of an overview of
news and articles related to EUginius. Below this article overview you can see
the total number of GMOs, methods and reference materials, with links to all of
them.
[GMO
count] GMOs (incl. stacks) links to the List with
GMOs and their identifiers page. For more information on this page, consult 3.1.1 List with GMOs and their identifiers.
[method
count] methods links to the Detection methods search
result page, with no search criteria. For more information on this page,
consult 3.2.1 Detection Methods.
[reference
material count] reference materials links to
the Reference material search result page, with no search criteria. For more
information on this page, consult 3.2.3.2
Reference material search result.
Genetic elements links to the List with
GMOs and genetic elements page, with the element tree expanded and detailed
element information. For more information on this page consult 3.1.3 List with GMOs and genetic element.
Below the Genetic elements link you can
find a link to an up-to-date list of GMO-related
websites.
A link to a list of GMO-related websites
is found below this. At the bottom of the taskbar are hyperlinks for giving
input or feedback (see 5.1
Input and Feedback).
2.2.1.2
Homepage body (center)
The top section, titled The European GMO database, gives general
information on EUginius.
The section titled Free-text search has two different modes of use, GMO search and
Literature search. Both work with the same search bar. Additionally, advanced
searches are available at the links below the search buttons. For more
information on this section, consult 2.3 Homepage
Search section.
EUginius is a collaboration between
institutes. The section titled About the
partners lists all members of the EUginius consortium. The more about the partners... hyperlink in
this section brings you to a separate page with more detailed information on
the members.
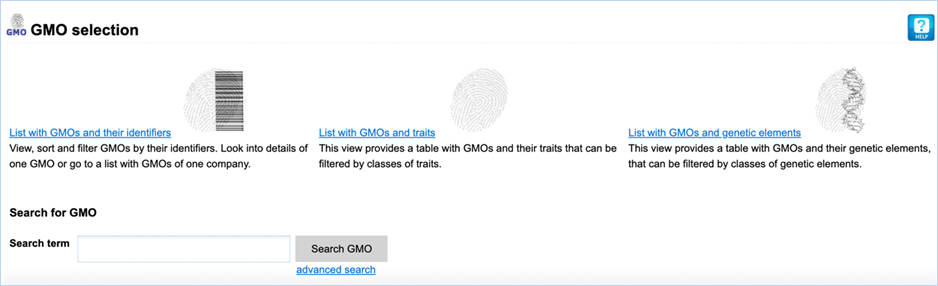
Figure 2 - GMO module sections
The GMO module provides you with four
different sections (Figure
2). They
all allow you to search for GMOs using different criteria.
List with GMOs and their identifiers
lets you view, sort
and filter GMOs by their identifiers. It shows the name, UID, species, traits,
companies, developers, tradenames and EU authorisation of GMOs.
List with GMOs and traits provides you with GMOs and their
associated traits. It shows the name and traits of a GMO and offers additional
filtering for these traits. The traits are organized in a hierarchical tree
(Trait thesaurus).
List with GMOs and genetic elements provides you with GMOs and their
genetic elements. It shows the name and all genetic elements of GMOs while
offering additional filtering for these genetic elements. The genetic elements
are organized in a hierarchical tree (DNA thesaurus).
The Search for GMO section is a free-text
search which scans the List with GMOs and
their identifiers section for any matching terms. All other sections use a
query-building search.
For more information on this module, consult 3.1 GMO.
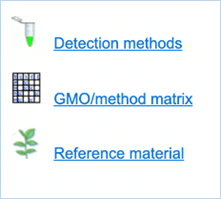
Figure 3 - Detection module sections
The Detection module provides you with three
different sections (Figure
3).
All sections in this tab provide you with information regarding GMO detection.
Detection methods lets you search PCR
methods designed for GMO screening, identification and quantification.
GMO/method matrix lets you find information on the
specificity of PCR methods and their abilities to detect GMOs. A set of methods
can be selected and filtered by specific criteria. You are then given a table
displaying the verification data.
Reference material lets you search for GMO reference
materials and provides concentrations, percentages and catalogue numbers with
sources.
For more information on this module, consult 3.2 Detection.
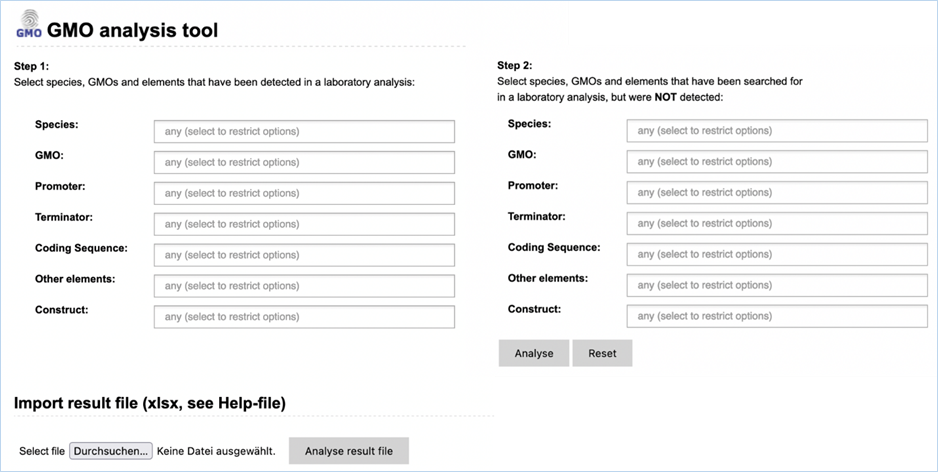
Figure 4 - Analysis module
The Analysis
module (Figure 4) consists
of fourteen input fields containing information on GMO detection results. It
supports you in sample analysis and provides explanations for detected elements.
Import result file lets you import an
Excel file with screening outcomes, saving you from entering data manually.
For more information on this module, consult 3.3 Analysis.

Figure 5 - Authorisation module sections
The Authorisation module
provides you with three different sections (Figure
5).
All sections in this tab provide you with information regarding GMO approval
status.
Search for generic approval is a query-building
search which lets
you find information on the approval status of a specific GMO for use in food,
feed, cultivation or other uses.
Custom Search - EU applications is a query-building
search which lets
you find detailed information on applications that were submitted for GMOs with
information on intended use, legal status, and legislation.
The Search
term section is a free-text search which works independently of the other two
sections. Result table shows application reference number, species, GMO, UID,
intended use and EU authorisation status, applicants, commission decision
number, expiry date, decision date, legislation, traits, genetic elements, tradenames,
and companies/institutions. The matching search terms are highlighted.
The Search module lets you do a free-text
keyword search on GMOs and literature. An advanced search option is also
available for GMOs and literature. Additional search options are available for
authorisation, methods, reference material and genetic elements with an extra free-text
search being possible for genetic elements.
For more information on searching in
EUginius, consult 3.5 Search.
2.3 Homepage
Search section
The homepage free-text search section has
two different modes of use, GMO search and Literature search. Both work with
the same search bar but advanced searches are available at the links below the
search buttons. More search types are available on the Search module tab in the menu, for information on this tab or on
search results consult 3.5
Search.
|
|
Tip:
In the Search module tab, you
can click on Element search to find GMOs, DNA inserts, donors and traits
which are attributed to certain elements. For more information on this
consult 3.5.3 Element Search
|
|
The standard free-text
GMO search can find GMO, UID, tradename, species, company and traits.
Advanced
GMO search presents you with seven fields, these
correlate to the above mentioned six features and also genetic elements.
The main advantage of the advanced search is filtering out unwanted results, as
it allows exclusion of stacked events and closer specification of search terms.
The advanced search is a query-building search as opposed to a free-text
search.
Some examples of free-text searches and search terms are listed below:
|
|
|
Search Term(s)
|
Finds GMOs with
|
|
Bt*
|
names "Bt11", "Bt10 maize", "BT10
potato", "FR-Bt1", etc.
|
|
305423
|
with
UID "DP-3Ø5423-1"
|
|
MON 00810 6
|
UID "MON-ØØ81Ø-6"
|
|
RRS
|
alias
"RRS" (=GTS 40-3-2)
|
|
zea
|
species "Zea mays"
|
|
soybean
|
species
"Glycine max"
|
|
syngenta
|
UID "Syngenta Seeds, Inc"
|
|
yieldgard
|
tradename
"YieldGard VT PRO", "Yieldgard™",
"Maxguard/Yieldgard", etc.
|
|
bt11
|
name "Bt11" and stacks containing Bt11
|
|
insect
|
trait
"Insect resistance"
|
|
|
For more information on search functions
or tips for search strategies, consult 3.5 Search.
The standard free-text
literature search can find GMO name, abstract, citation and keywords.
The advanced
Literature search presents you with three search options: GMO, Genetic
Element and DNA search. Each of these include a search field for name, publishing
authority and publication date. Keywords entered in other sections will not be
taken into account when you click the search button (see example). The main
advantage of the advanced search is filtering out unwanted results, as it allows
closer specification of search terms. The advanced search is a query-building search
as opposed to a free-text search.
|
|
Example:
If you hit search
on the DNA search section, only data in this section will be taken into
account. Any data entered in GMO or Genetic Element search will be ignored.
|
|
For more information
on search functions or tips for search strategies, consult 3.5 Search.
 The
Help module provides you with this
user manual. It can be accessed from several modules by clicking the blue help
button in the top right corner.
The
Help module provides you with this
user manual. It can be accessed from several modules by clicking the blue help
button in the top right corner.
Clicking the blue help button while in a
module will take you to the matching section of this manual.

Figure 6 - GMO module sections
When entering the GMO module, you are presented with four
different sections (Figure
6).
All sections in this tab allow you to filter and search for GMOs using
differing criteria.
The Search for GMO function is identical to the homepage GMO search function.
For more information on this search function consult 3.5.1 GMO Search.
3.1.1 List with GMOs and their Identifiers
List with GMOs and their identifiers
lets you view, sort
and filter GMOs by their identifiers. It shows the name, UID, species, traits,
companies, developers, tradenames and EU authorisation of GMOs (Figure 7).
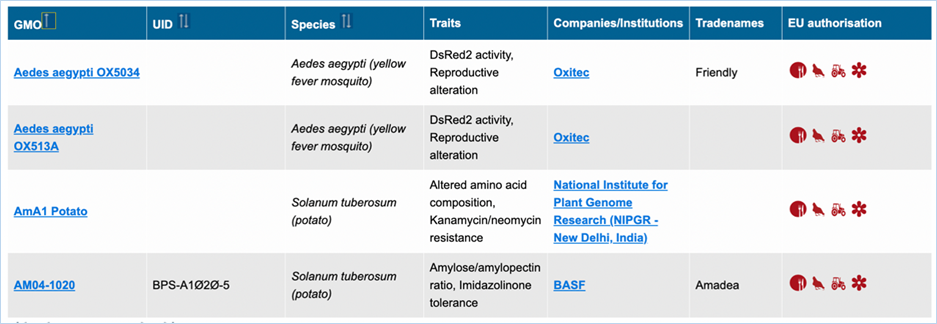
Figure 7 - Result of list with GMOs and
their identifiers
|
1.
|
GMO
|
Most commonly used name for the
GMO
Clicking
the GMO name will lead you to the GMO
detailed information page. For more information on this page consult 3.1.4 GMO detailed
information.
|
|
2.
|
UID
|
The (UID) Unique Identifier
which is given to the GMO.
This
is useful in gathering information from other databases
|
|
3.
|
Species
|
Species which the organism
belongs to.
|
|
4.
|
Traits
|
A list of traits expressed by
the GMO which are not found in the wild species.
|
|
5.
|
Companies
|
All companies producing the
GMO.
Clicking the company name will lead you to the list of
all GMOs related to (or produced or
sold by) this company
|
|
6.
|
Developers
|
The institute(s) or
company(ies)that developed the GMO, if available.
|
|
7.
|
Tradenames
|
The name which the GMO is
commonly sold under by companies.
|
|
8.
|
EU Authorisation
|
Approval status of the GMO for
food, feed, cultivation and other uses.
Clicking
the icon in the table will lead you to a list with the EU applications
of this GMO (if available)
Additional information on EU authorisation
can be found in the
Authorisation
tab. For more information on this, consult 3.5
Authorisation.
|
Applying a filter can be
done by clicking the apply filter hyperlink
at the top of the page. This will take you to the Advanced GMO search. For more information on this consult 3.5.1.1
Advanced GMO Search.
Sorting
and Navigating Pages can be done using the arrows,
for an explanation on navigating search results consult 3.5.4
Navigating Search Results.
3.1.2 List
with GMOs and Traits
List with GMOs and traits provides you with GMOs and their
associated traits. It shows the name and traits of a GMO and offers additional
filtering for these traits.
|
1.
|
GMO
|
Most commonly used name for the
GMO
Clicking
the GMO name will lead you to the GMO
detailed page. For more information on this page consult 3.1.4 GMO
detailed information.
|
|
2.
|
Traits
|
A list of traits expressed by
the GMO that are not found in the wild species.
|
3.1.2.1
Navigating the traits page
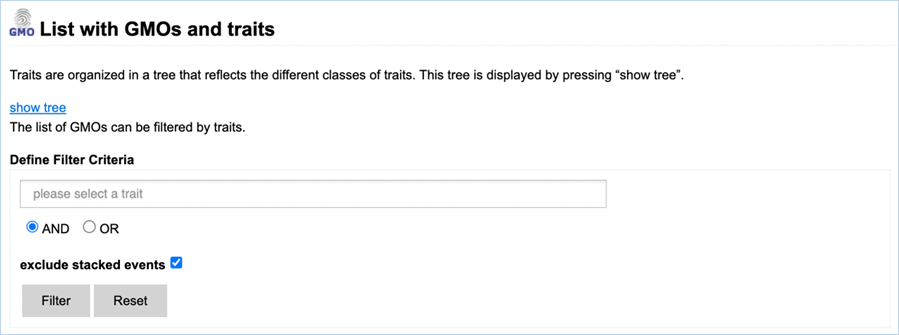
Figure 8 -
Defining filter criteria to find GMOs with specific traits.
Filtering Data can be done through the select a trait field (Figure 8). When
clicking the field, you are presented with a drop-down list. A trait from this
drop-down list can be selected by clicking it, adding it to the query. By
typing text into the field, the shown traits will be limited to traits matching
the search term. One or more traits from the drop-down list can be selected.
A selection of
traits can also be made through the traits tree.
The
Traits Tree is opened by clicking the show tree hyperlink at the top of the page. This
presents you with a list of categories with  next to them (Figure
9).
Clicking the
next to them (Figure
9).
Clicking the  will add the category to the searched traits, clicking the category
will expand it, showing subcategories or specific traits. See example below:
will add the category to the searched traits, clicking the category
will expand it, showing subcategories or specific traits. See example below:
|
Example:
Here the main category (1) has been expanded by clicking
it. The subcategory under this (2) was also opened, displaying the traits (3).
Any of these parts can be filtered for by clicking the
plus symbols next to them. This will add them to the filter field
|

Figure 9 - Part of traits tree
|
Filter options can be adjusted by
selecting either AND or OR. AND will filter for GMOs that possess all specified
traits while OR will filter for GMOs that possess any of the traits. By default,
stacks are excluded. Including stacked events can be done by unchecking the box
next to Exclude stacked events.
Sorting
and Navigating Pages can be done using the arrows,
for an explanation on navigating search results consult 3.5.4
Navigating Search Results.
3.1.2.2
Search Results

Figure 10 - Search results GMOs and
traits
After filtering you get a list of GMOs and
traits (Figure 10).
Clicking the GMO name will bring you to the GMO details tab, for more
information on this consult 3.1.4 GMO
detailed information. In the traits-column each row of text in a
cell represents one trait exhibited by the GMO.
|
|
Example:
EF2-114 expresses two traits as result of genetic
modification: reduced ethylene synthesis, which falls in the category altered
ripening or flowering within the category alteration in growth, development
or product quality, and Altered carotenoid biosynthesis which is in the Colour
modification category within the main category Composition alteration.
|
|
3.1.3 List
with GMOs and Genetic Element
List with GMOs and genetic elements provides you with GMOs and their
genetic elements. It shows the name and all genetic elements of GMOs while
offering additional filtering for these genetic elements.
|
1.
|
GMO
|
Most commonly used name for the
GMO
Clicking
the GMO name will lead you to the GMO
detailed information page. For more information on this page consult 3.1.4 GMO
detailed information.
|
|
2.
|
Genetic Elements
|
A list of all elements involved in genetic modification of the GMO.
|
3.1.3.1 Navigating the Genetic
Elements page
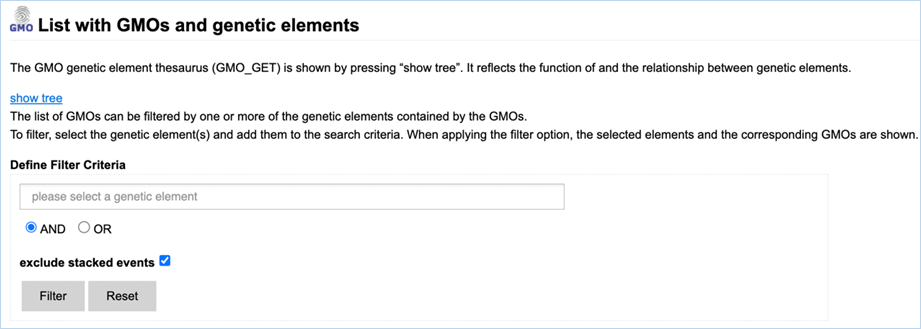
Figure 11 - Define filter criteria to
find GMOs containing specific genetic elements
Filtering Data can be done through the select a genetic element field (Figure
11).
When clicking the field, you are presented with a drop-down list. An element
from this drop-down list can be selected by clicking it. Limiting the list of
shown elements in this drop-down list can be done by entering text into the
field.
A selection of elements
can also be made through the genetic elements tree.
The
Genetic Element Tree is opened by clicking the show tree hyperlink at the top of the page. This
presents you with a list of categories with  next to them (Figure
12).
Clicking the
next to them (Figure
12).
Clicking the  will add the category to the searched traits, clicking the category
will expand it, showing subcategories. See example below:
will add the category to the searched traits, clicking the category
will expand it, showing subcategories. See example below:
|
Example:
Here the main level (1) has
been expanded by clicking it. A corresponding Level 2 below (2) was also
opened, displaying the genetic elements (level 3).
Any of these parts can be
filtered for by clicking the plus symbols next to them. This will add them to
the filter field
|
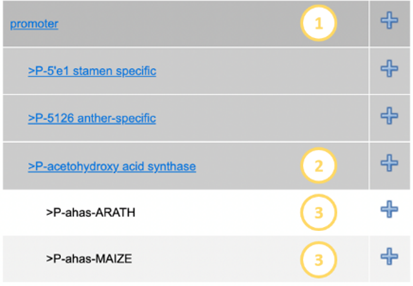
Figure 12 - Part of genetic elements tree
|
By clicking show
tree details next to hide tree EUginius
will display more information about the elements in the tree (Figure
13). Synonyms displays other names for the
element, Donor shows the organism
from which the element is taken, Trait
shows the trait that the element confers to the GMO, Function gives the element’s function in the GMO and Definition gives the unabbreviated name
of the element. BCH gives record IDs
of the corresponding elements in the Biosafety Clearing-House (http://bch.cbd.int).
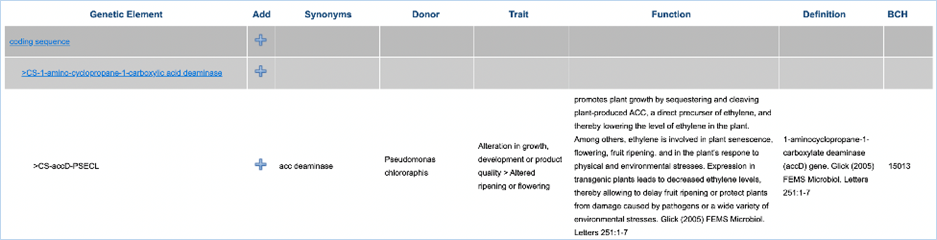
Figure 13 - Details of a genetic element
Filter options can be adjusted by
selecting either AND or OR. AND will filter for GMOs that possess all specified
elements while OR will filter for GMOs that possess any of the elements. By
default, stacks are excluded. Including stacked events can be done by unchecking
the box next to Exclude stacked events.
Please note: The
tree has a hierarchical structure where lowest levels are related to a unique
higher level.
The highest level (level_1)
describes the general functional types of the genetic element. The next level
(level_2) is composed of an abbreviation of the element type plus a generally
comprehensive long name referring to the detailed biological function. Below
level_2, genetic elements of common/homologous origin and/or with
comparable/analogous features are grouped. Those level_3 terms serve as a label
for the actual genetic elements.
When you select a higher level, all the
elements belonging to lower linked levels will be considered in the search.
3.1.3.2
Search Results
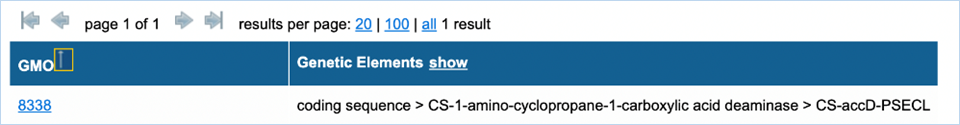
Figure 14a - Search results GMOs and
genetic elements
After filtering you get a list of GMOs and
genetic elements (Figure
14a).
Clicking the GMO name will take you to the GMO details tab, for more
information on this consult 3.1.4 GMO
detailed information. By default, only the filtered genetic
elements are shown, but by pressing show in the heading of the table you can
bring up all genetic elements associated with the GMOs in alphabetical order
(Figure 13b).
|
Example:
Above, filtering happened for CS-accD-PSECL (which is
related to Coding Sequence > CS-1-amino-cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
deaminase). By default, the genetic element column only shows the filtered
element. By hitting show
all associated elements for the GMO can be shown (below).
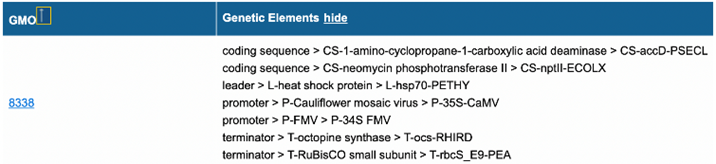
|
Figure 14b – Part of Search results GMOs and genetic elements with
the activated show function
Sorting and Navigating
Pages can be done using the arrows, for an
explanation on navigating search results consult 3.5.4 Navigating Search Results.
3.1.4 GMO Detailed information
When
clicking the name of a GMO in any of the EUginius sections, you will be
redirected to GMO detailed information tab
(Figure
15). This tab presents you with
all information which is linked to the selected GMO. Displayed tables can be
exported into MS-Excel.
3.1.4.1
Navigating GMO Detailed Information
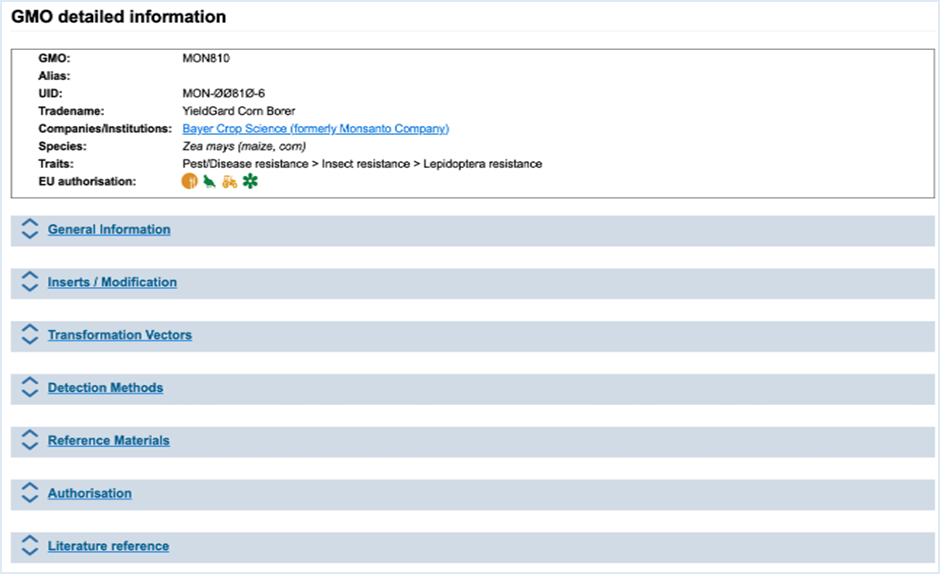
Figure 15 - GMO detailed information
The basic information on the GMO is always
shown at the top. This information includes GMO name, Alias, UID, Tradename, Company,
Developer, Species, Traits and EU authorisation. Company also provides a link
which brings you to the GMO Identifier List. This list will exclusively show
GMOs which the company has produced. Clicking the traffic light authorisation
symbols takes you to the GMO-specific authorisation details, which provides the
same information as EU Application Details Search, with your GMO as filter. For
more information on the application details, consult 3.5.3 Search for EU Application details.
By clicking the arrows, text or blue bar
the sections described below will expand, revealing additional information.
GMO detailed information tab
|
General
Information
|
General
information on GMO
|
|
|
Inserts
/ Modification
|
Modification
of the GMO on the molecular level / Sequence information when available
|
|
Transformation
vectors
|
Vectors
used to transform the GMO
|
|
Detection
Methods
|
Methods
to detect the GMO
|
|
|
Reference
Materials
|
Material
with known concentrations of the GMO
|
|
|
Authorisation
|
Approval
status of the GMO in the European Union
|
|
|
Literature
reference
|
Literature
describing the GMO
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.1.4.2
General Information
General
Information provides basic information on the
nature of the genetic modification and provides links to sources of information
regarding the GMO (Figure
16).
For an explanation of the module consult the image and table below.

Figure 16 - Explanation of general
information about a GMO
|
1.
|
Description
|
General overview of the GMO.
|
|
2.
|
Links regarding to this
GMO
|
Hyperlinks to sources, relevant documents and databases regarding
the GMO.
|
|
3.
|
Transformation /Modification
technique
|
The transformation or modification technique used to develop an
organism may differ. EUginius currently includes 15 techniques.
For more
information on these techniques consult for example: Ramkumar T.R., Lenka
S.K., Arya S.S., Bansal K.C. (2020) A Short History and Perspectives on Plant
Genetic Transformation. In: Rustgi S., Luo H. (eds) Biolistic DNA Delivery in
Plants. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2124. Humana, New York, NY.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0356-7_3
|
3.1.4.3 Inserts / Modification
Inserts
/ Modification provides more detailed information
on the nature of the genetic modification (Figure
17). Here
you can find elements in the composite DNA and all of EUginius’ sequences
associated with the GMO. For an explanation of the module, consult the image
and table below.
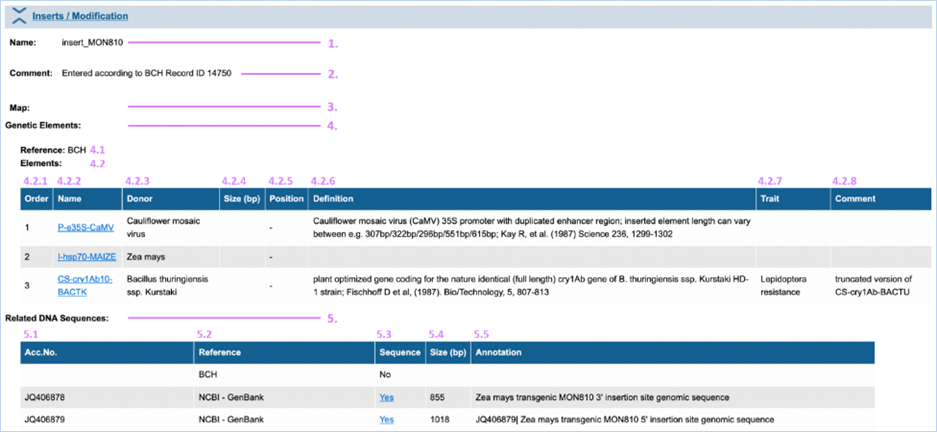
Figure 17 - Explanation of the
inserts/modification section
|
1.
|
Name
|
DNA called insert_ has
been confirmed in the GMO. DNA starting with vector_ describes the vector that was used for the transformation.
DNA ending with (putative)
describes information about the insert, based on the transformation vector.
|
|
2.
|
Comment
|
Contains more detailed information on the insert/insertion site.
e.g.
deletion, rearrangements, insertion etc.
|
|
3.
|
Map
|
If a DNA map is available this will be inserted here in a picture
format. Please note that this function is not used until now due to copyright
issues.
|
|
4.
|
Genetic Elements
|
Information following this header regards the elements contained
in the insert/vector
|
|
4.1
|
Reference
|
The source used for obtaining information about the insert which
the element belongs to.
e.g. scientific
journal or organisation
|
|
4.2.
|
Elements
|
All elements in the insert/vector with general data.
|
|
|
4.2.1 – 4.2.8
|
A summary of the element, as also described on the Genetic Element
Information page. If available the order of elements in the insert/vector is
also provided 4.2.1).
Clicking
the element name (4.2.2) will take you to Genetic Element Information, for
more information on this consult 3.1.5.1 Genetic Element
details.
|
|
5.
|
DNA Sequences
|
All sequences associated with the GMO and general data.
|
|
|
5.1 – 5.5
|
A summary of the available sequences, as also
described on the Sequence String Information page. The Sequence column (5.1)
can link you to additional information. This either says No if no sequence is available, or Yes if a sequence is available. If it says Yes this is also a hyperlink to
said sequence.
If you click Yes it will take you to the sequence string page. For more
information on this consult 3.1.5.2
Sequence String.
|
3.1.4.4
Transformation vectors
Transformation
Vectors provides more detailed information on the
vector used for the development of the GMO. For an explanation of the module
consult the paragraph above: 3.1.4.3 Inserts
/ Modification.
3.1.4.5 Detection Methods
Detection Methods provides a detection
search, with your GMO as filter. The additional column Verification is added on the right and displays method verification
for your GMO. Values in this table can range from 1 to 3 with the following
meaning:
1:
Detection of the target is
based on other information in EUginius (database, plasmid map etc.)
2:
Detection of the target is
verified by sequence alignment
3:
Detection of the target is
experimentally verified using reference material
For more information on the detection
methods table, consult 3.2.1 Detection Methods. For
more information about the verification values, consult 3.2.2 GMO/method
matrix.
3.1.4.6 Reference Materials
Reference
Materials provides a smaller version of the Reference Material search with your GMO
as filter. For more information on the Reference Material search section,
consult 3.2.3 Reference
Material. Clicking the
catalogue number will bring you to the GMO
reference material page, which provides you with extra information on the
reference material. For more information
on the GMO reference material page,
consult 3.1.5.3
Reference Material Details.
3.1.4.7
Authorisation
Authorisation provides detailed information on
applications that were submitted for the GMO with information on intended use,
legal status and legislation.
Clicking the Application reference number will
take you to the GMO application page.
For more information on this, consult 3.1.5.4 Application Details.
3.1.4.8
Literature reference
Literature
reference provides the same information as advanced Literature search, with your
GMO as filter.
Clicking the article citation will take
you to the GMO literature details
page. For more information on this, consult 3.5.2.3 Literature Details. For more
information on the Literature search section, consult 3.5.2
Literature Search.
3.1.5.1 Genetic Element details
Clicking the element name will take you to
the tree with genetic elements, with the selected element in focus. More
information about the tree can be found on the 3.1.3.1 Navigation the genetic elements
page.
Clicking Yes in
the Sequence column in the Related DNA Sequences
table of Inserts / Modification or Vector brings you to the Sequence string
page (Figure 18), this gives information on the sequence and provides the Sequence String.
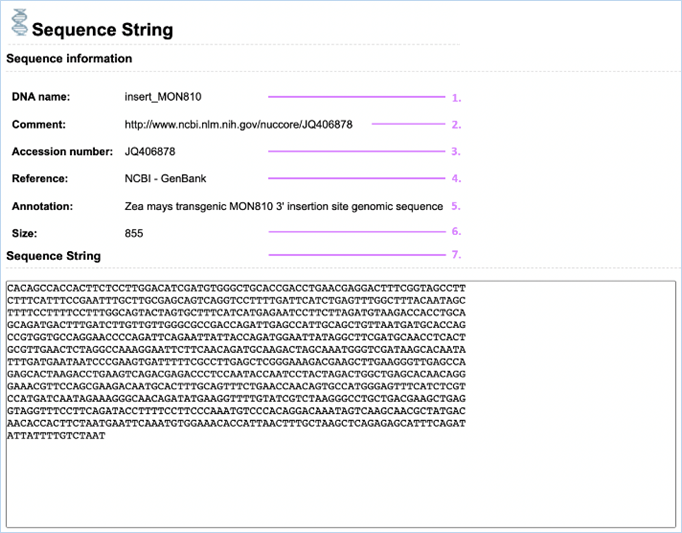
Figure 18 -
Explanation of sequence information
|
1.
|
DNA Name
|
DNA called insert_ has
been confirmed in the GMO.
DNA starting with vector_ describes
the vector which was used for the transformation. DNA ending with (putative) describes information about
the insert, based on the transformation vector.
|
|
2.
|
Comment
|
This field is often used for description of the source of the
information/detailed information on nucleotide changes in the insert.
|
|
3.
|
Accession Number
|
This is a unique code for genetic sequences, it can be used to
search for genetic sequences online
e.g.
GenBank
|
|
4.
|
Reference
|
The source used for entering the composite DNA into EUginius.
e.g. NCBI
– GenBank, BCH, BVL or WFSR
|
|
5.
|
Annotation
|
The name under which the sequence is annotated in the reference database/source.
|
|
6.
|
Size
|
The size of the sequence in base pairs (bp).
|
|
7.
|
Sequence String
|
The full sequence as given in the reference.
|
3.1.5.3 GMO Reference Material
The GMO Reference Material page displays the
GMO detailed information header with general information on the GMO.
Below this is a smaller version of the Reference
Material search with your GMO as filter. For more information on the
Reference Material search section, consult 3.2.3 Reference Material.
Clicking the
catalogue number will bring you to the material details page (Figure 19), which provides you with extra information on the reference
material.
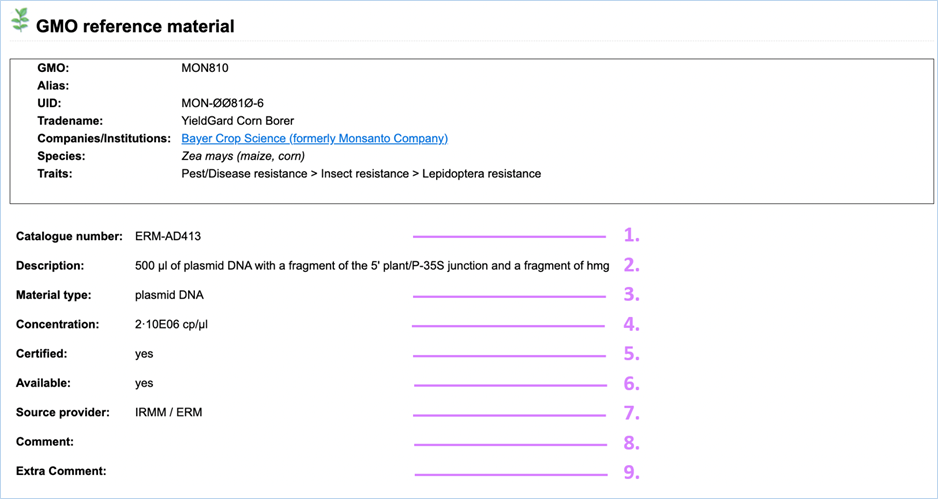
Figure 19 – Explanation
of GMO reference material
|
1.
|
Catalogue number
|
A unique identifier given to the reference material by the
material provider. This identifier is used for ordering the material.
|
|
2.
|
Description
|
A description of the reference material stating material amount
and type.
|
|
3.
|
Material Type
|
The type of material.
Reference
material can vary from dried powder to DNA or even bacterial strains.
|
|
4.
|
Concentration
|
Concentration of the reference material.
cp/µl is the measure for DNA concentration,
it refers to genome copies (or haploid genome equivalents) per microliter
|
|
5.
|
Certified
|
Certified material comes with a certificate proving the material’s
quality and composition.
|
|
6.
|
Available
|
Indicates availability of the reference material at the source
provider.
|
|
7.
|
Source Provider
|
The institution which provides the reference material.
This can
be AOCS, EURL (JRC), Eurofins GeneScan, IRMM/ERM, SIGMA - ALDRICH or the Pasteur Institute.
|
|
8.
|
Comment
|
Any additional notes which EUginius staff have about the DNA are
added here. This field is often used for hyperlinks/references.
|
|
9.
|
Extra Comment
|
The
Extra Comment field is to indicate issues with the material in combination
with specific method(s) (e.g. unexpected positive signal).
|
3.1.5.4 Application Details
The GMO application page can be accessed by
clicking the Application reference number hyperlink in the Authorisation table. It displays the GMO Details header with general
information on the GMO.
Below this, there are three sections: Application details (Figure 20), a Use/Status
table and Documents.
Application Details shows general
information on the application.

Figure 20 -
Explanation of application details
|
1.
|
Application reference number
|
A unique identifier for the application, assigned to it by the
institute which received the application.
e.g.
for applications under Regulation (EU)
No 1829/2003: EFSA-GMO-Country-Year-Number
|
|
2.
|
Country
|
The country/region for which the approval applies.
|
|
3.
|
Applicant
|
Company/institution which submitted the application.
|
|
4.
|
Legislation
|
Legislation under which the ruling was made.
|
|
5.
|
Comment
|
Any notes which EUginius staff have about the application are
added here. This field is often used for short summaries on related
applications.
|
|
6.
|
Decision date /Expiry
date
|
The period in which the decision applies.
|
|
7.
|
Related applications
|
Hyperlinks or application references for previous applications of
this GMO and use-combination.
|
|
|
|
|
The Use and Status table shows intended
uses and approval status for said uses.
Attached Documents can be found below in the Documents table, this generally includes
the summary of application, EFSA or EU Scientific Panel and EFSA risk
assessments and decision documents with any other documents the EUginius staff
deemed relevant.
Figure 21 - Functions in the Detection module
When entering the Detection section, you
are presented with three different functions (Figure
21).
All functions in this tab provide you with information regarding GMO detection.
3.2.1 Detection Methods -> PCR methods for GMO
detection and identification
3.2.1.1
All methods for one GMO
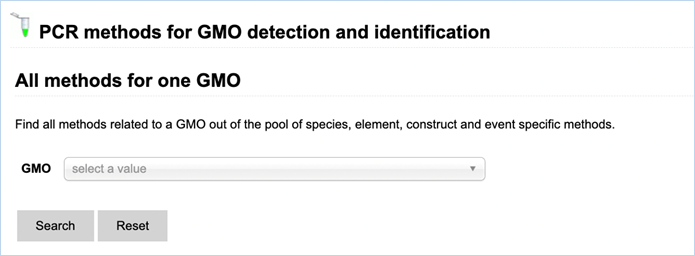
Figure 22 - Search
All methods for one GMO with GMO drop-down list
The methods
search for one GMO (Figure 22) enables finding methods, related to a specific
GMO, out of the pool of species-, element-, construct- and event-specific
methods by selecting this GMO in the drop-down list.
Names of detection methods in EUginius
have a specific syntax. Methods designed for quantification have the prefix QT-
(quantitative), methods starting with QL- (qualitative) have been designed for
qualitative analysis. This prefix is followed by a three-letter code: -CON-
stands for construct-specific, -ELE- is an element-specific method, -EVE-
indicates an event-specific method, and -TAX- is a taxon-specific method. If
relevant, the species code (e.g. ZM – Zea
mays, GM – Glycine max, and 00 if
species is not relevant) is added to the method’s name. The last part indicates
the primers used, or, for methods that are common with GMOMETHOD database (https://gmo-crl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/gmomethods/),
only consist of a three-digit number.
3.2.1.2
Free-text
search for methods
The standard free-text
detection method enables searching for detection methods based on the name of
the method, the primers or the probe or based on the sequence of the primers,
of the probe or of the amplicon. The search results will also provide you with
the Amplicon Size, but this is not a searchable metric.
In EUginius’ free-text
searches at least one word will need to match the search term. Parts of a word
matching will not be picked up. e.g. searching for “VW0” will not show MON810 primers VW01 or VW03. Searching for ”event”, however, will show all
event-specific methods, as EUginius views phrases with hyphens as two separate
words.
Wildcards give
you results when you only know part of a keyword. The wildcard symbol in
EUginius is *.
For example, searching for “VW*” will show all data containing “VW” even
without a full word match (i.e. VW01, VW03). Wildcards can be added to both
left and right sides of the word. A wildcard on the left will only apply to
additional characters to the left, a wildcard on the right will only apply to
the right.
Clicking advanced
search on
the search results page will take you to the main Detection Methods page.
3.2.1.3
All methods corresponding to defined
criteria
Based on the selected search and dependent
on filter criteria chosen you can find PCR methods for your specific query and
your desired applications: GMO screening, identification and quantification
(Figure 23).

Figure 23 -
Preselect a method set
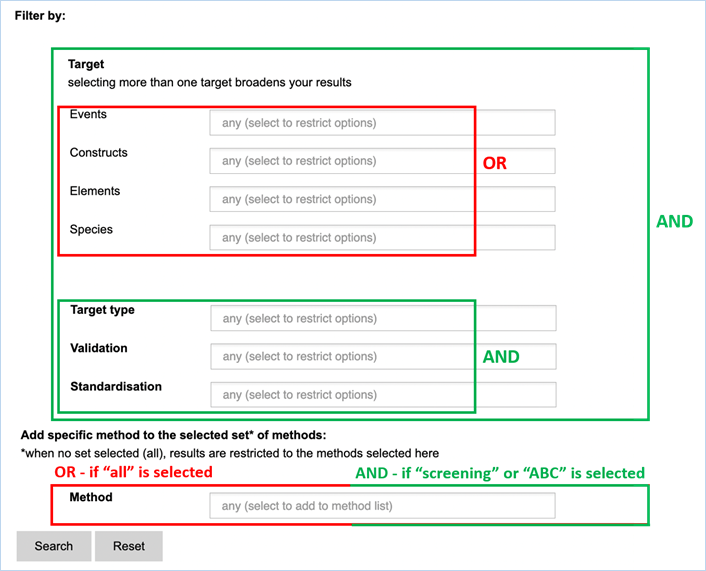
Figure 24 - Define a query for
specific methods
For filtering, EUginius makes use of
Boolean operators, specifically AND and OR.
AND requires all provided keywords to match the search results,
narrowing down the number of results.
OR means you are shown all
results that match either of the keywords, broadening the number of results.
The Target fields Events, Constructs,
Elements and Species are all OR operators. The fields Target type, Validation
and Standardisation are AND operators to restrict the list. If multiple
keywords are entered in fields Target type, Validation and Standardisation at
least one of those keywords have to be present (Figure 24).
Any
method entered in the Method field will automatically show up in the search
results additionally to the methods of the set (Screening or ABC). If no method
set has been selected (=ALL) only the method(s) selected in the Method field
will show up.
Below, you can find the meaning of all
keywords that can come up in your detection methods searches (Figures 23 and 24).
ALL
SCREENING
|
A set of
methods which is restricted to methods designed to detect GMOs.
|
ABC
|
Set of
screening methods which is constantly checked and adjusted by the German
National Reference Laboratory (NRL) in collaboration with the national
network of GMO laboratories.
|
EventS
|
One or more
events from this drop-down list can be selected by clicking. Limiting the
list of shown events in said drop-down list can be done by entering text into
the field.
The drop-down
list contains all events that EUginius has detection methods for.
|
ConstructS
|
One or more
constructs from this drop-down list can be selected by clicking. Limiting the
list of shown constructs in said drop-down list can be done by entering text
into the field.
The drop-down
list contains all constructs that EUginius has detection methods for.
|
ElementS
|
One or more
elements from this drop-down can be selected by clicking. Limiting the list
of shown elements in said drop-down list can be done by entering text into
the field.
The drop-down
list contains all elements contained in EUginius.
|
Species
|
One or more
species from this drop-down list can be selected by clicking. Limiting the
list of shown methods in said drop-down list can be done by entering text
into the field.
The drop-down
list contains all species that EUginius has detection methods for.
TARGET Type
One or more target types from this drop-down list can be selected
by clicking.
|
Construct-specific
|
Specific for
detecting the presence of two elements that are in proximity.
|
|
Element-specific
|
Specific to a
single element.
|
|
Event-specific
|
Specific to a
single GMO.
|
|
Taxon-specific
|
Specific to an
entire taxon.
|
|
One or more validations
from this drop-down list can be selected by clicking.
|
In-house
validation
|
The method has
been validated in one laboratory using reference materials as sample.
|
|
Ring validation
|
The method's
performance (sensitivity, specificity, repeatability, reproducibility) has
been evaluated using identical samples in several laboratories under control
of a supervising laboratory.
|
|
Unknown
|
Validation of the
method is unknown or the method is not validated.
|
One
or more standardisations from this drop-down list can be selected by clicking.
|
CEN standard
|
Standardised by
the European Committee for Standardisation (CEN).
|
|
EU reference
method
|
Standardised by
the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission or the EU-RL GMFF.
|
|
ISO standard
|
Standardised by
the International Organization for Standardization.
|
|
National standard
|
Performed
according to national standards (country not specified).
|
|
One or more
methods from this drop-down list can be selected by clicking. Limiting the
list of shown methods in said drop-down list can be done by entering text
into the field.
The drop-down
list contains all methods in EUginius.
|
|
Figure 25 shows
an example of the result of a specific query. For more explanation about the
different columns see above. The content of the table can be exported as an
Excel file (see section 3.6 Exporting data).
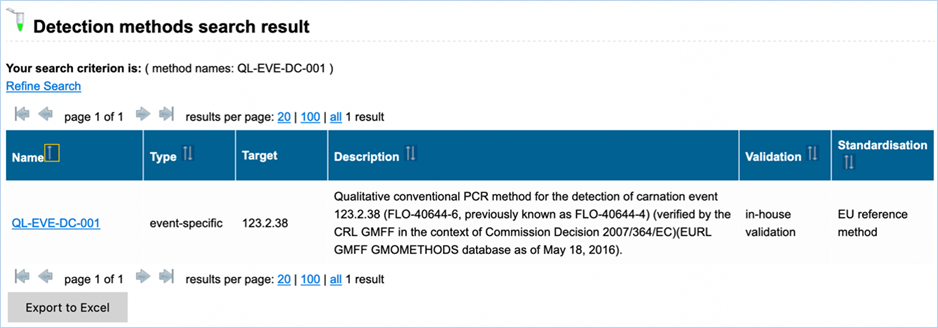
Figure 25 - Result of detection method search
|
Detailed
examples on how to use the functions in the detection module can be found in 4.1 Detection: search workflow for detection methods.
The GMO/method
matrix section lets you find information on the specificity of a PCR method and its ability
to detect GMOs (Figure 27). A set of methods can be
selected and filtered by specific criteria. You can also select specific GMOs
and/or species of interest or filter for GMOs with a specific authorisation
status in the EU. If no GMOs are selected and no status filter applied the
matrix will contain all GMOs present in EUginius.
3.2.2.1 Select methods foR the
GMO/method matrix
The Filter Criteria for Select methods for the GMO/method matrix section
lets you limit the detection methods which are shown in the verification
matrix.
A detailed explanation of keywords and
combining them with AND or OR in the detection methods filter/search was given
in 3.2.1.3 All methods corresponding to defined criteria.
3.2.2.2 select GMOs for the GMO/method matrix
The Filter Criteria for Select GMOs for the GMO/method matrix section lets you
limit the GMOs which are shown in the verification matrix. You can select specific GMOs,
species of interest or filter for GMOs with a specific authorisation status in
the EU.
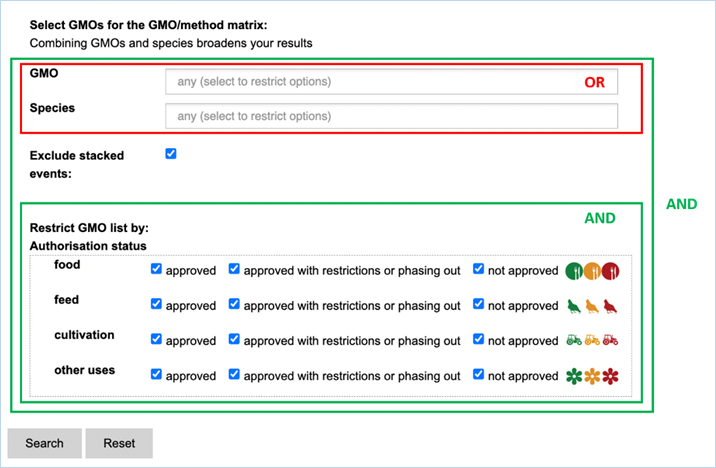
Figure 26 - Define a query for the GMOs
for the GMO/method matrix
For filtering EUginius makes use of
Boolean operators, specifically ‘AND’ and/or ‘OR’.
AND requires all provided keywords to match the results, narrowing
down the number of results.
OR means you are shown all
results that match either of the keywords, broadening the number of results.
The list of GMOs to be shown in the matrix
(Figure 27) can
be restricted by different filters (Figure 26).
Specific GMOs or Species can be selected.
Stacks can be excluded (default) or
included.
The list of GMOs can be restricted by
authorisation status. The authorisation options are combined with AND. This
means that GMOs in the list should comply with all the options.
By
hitting search EUginius will open up the option to show three result matrices,
which all can be exported as an Excel file (see section
3.6 Exporting
data).
·
GMOs detected by selected methods
·
GMOs not detected by selected methods
·
All GMOs
3.2.2.3
Navigating The Matrix
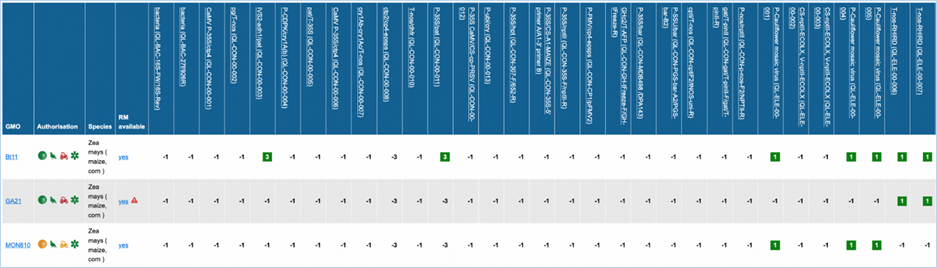
Figure 27 -
Verification matrix
Except for GMO, Authorisation, Species and
Reference material (RM) available, all column headers are detection methods in
EUginius. This list of detection methods can be limited by using filters in the
Select methods for the GMO/method matrix section
of the search page. For more information on this section consult 3.2.2.2 Select
methods for the GMO/method matrix.
All row headers are GMOs in EUginius. This
list of GMOs can be limited by using filters in the Select GMOs for the GMO/method matrix section of the search page.
For more information on this section consult 3.2.2.3 Select GMOs for the GMO/method matrix.
The matrix crosses filtered GMOs with
filtered detection methods, assigning a value to each GMO-method combination.
The values indicate the reliability with which a method will detect a certain
GMO. These values mean the following:
|
3
|
Detection of the
target is experimentally verified using reference material
|
|
2
|
Detection of the
target is verified by sequence alignment
|
|
1
|
Detection of the
target is based on other information in EUginius (literature, plasmid map
etc.)
|
|
-1
|
No expected target
detection, based on other information in EUginius (literature, plasmid maps
etc.)
|
|
-2
|
No expected target
detection, based on sequence alignment
|
|
-3
|
No target
detection is experimentally confirmed using reference material
|
In the GMO column, clicking a GMO’s name
will take you to the respective GMO details tab. For more information on this
tab consult 3.1.4 GMO detailed
information.
Authorisation uses coloured symbols to
display the approval
status of the GMO for food, feed, cultivation and other uses. For more
information on this, consult 3.5.1
Authorisation Symbols.
RM
available tells you about reference material availability. If it says Yes, this means reference
material is available, at this point the text is a hyperlink. Clicking the
hyperlink will take you to the Reference Material tab of GMO Details. For more
information on this tab, consult 3.1.4.5 Reference
Materials.
Specific examples on how to use the
functions in the GMO/method matrix module can be found in 4.2 GMO/method matrix: Optimisation of a screening
strategy and 4.3 GMO/method matrix: Designing a Screening strategy .
The Reference
material section allows
to perform searches on the availability and on the source of GMO reference
materials (Figure 28), providing you with the information you need to validate
or perform your experiments.
3.2.3.1
Searching
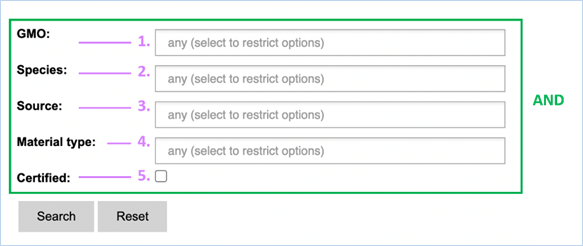
Figure 28 - Define a query for reference
materials
For its searches EUginius makes use of
Boolean operators, specifically AND and OR.
AND requires all provided keywords to match the search results,
narrowing down the number of results.
OR means you are shown all
results that match either of the keywords, broadening the number of results.
In the reference material search all
fields need to match reference material for it to be shown in the search
results. The search fields in this section are query-building searches.
Selecting two values in one field means EUginius puts an OR between the
keywords. This means that only one of the keywords has to match.
Below is a list with descriptions of the
search parameters.
|
1.
|
GMO
|
The name(s) of GMOs for which you want to find reference material.
|
|
2.
|
Species
|
The species for which you want to find reference material.
|
|
3.
|
Source
|
The institution which provides the reference material.
This can
be AOCS, EURL (JRC), Eurofins GeneScan, IRMM/ERM, SIGMA-ALDRICH or the
Pasteur Institute.
|
|
4.
|
Material Type
|
The type of material you would like to have as reference material.
Reference
material can vary from dried powder to DNA or even bacterial strains.
|
|
5.
|
Certified
|
Checking this box will mean only certified materials are shown.
|
3.2.3.2 reference material search
result
Figure 28 shows an
example of the result of a specific query. For more explanation about the
different columns, see the search criteria above (Figure 29). The column Value
is not a search criterion but indicates the concentration of the GMO in the
sample. The content of the table can be exported as an Excel file (see section 3.6 Exporting
data). Clicking catalogue number takes you to the details. For
more information on this page, consult 3.1.5.3 GMO reference material.
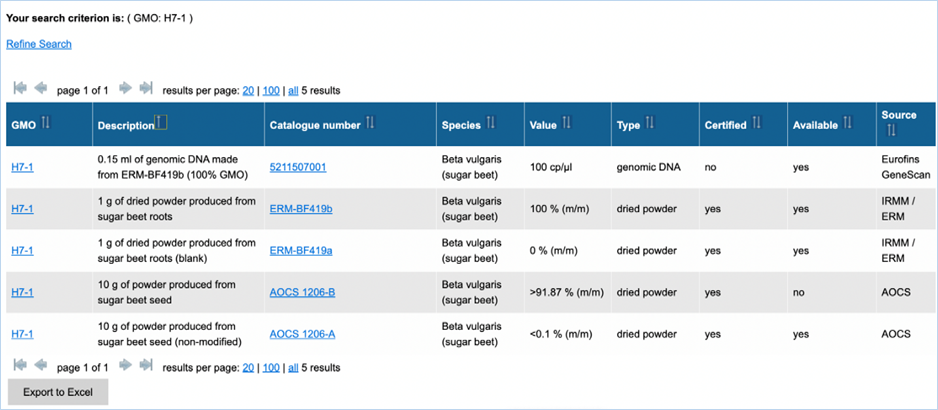
Figure 29 - Reference
material search result
The Analysis
module consists of 14 input fields containing information on GMO detection
results (Figure 30). It supports you in sample analysis and can provide
explanations for detected events. Import result file lets you import an Excel
file with screening outcomes from your laboratory, saving you from entering
data manually. A detailed example workflow showing how to use the functions
can be found in 4.4 Analysis Tool.
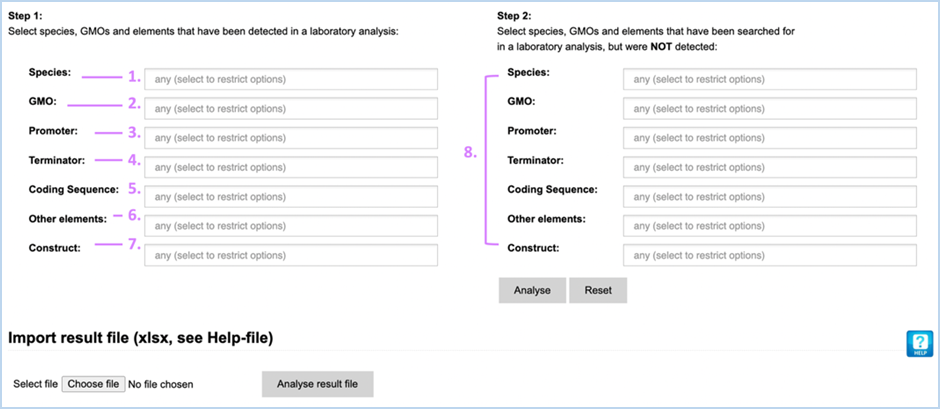
Figure 30 -
Manually entering screening data for Analysis module
The fields can be
filled with the following information:
|
1.
|
Species
|
Species detected with a taxon-/species-specific method.
|
|
2.
|
GMO
|
GMOs detected with an event-specific method.
|
|
3.
|
Promoter
|
Promoters detected with an element-specific method.
|
|
4.
|
Terminator
|
Terminators detected with an element-specific method.
|
|
5.
|
Coding Sequence
|
Coding sequences detected with an element-specific method.
|
|
6.
|
Other elements
|
Other elements detected with an element-specific method.
|
|
7.
|
Construct
|
Constructs detected with a construct-specific method.
|
|
8.
|
Step 2, NOT detected
|
Here you should enter any species-, GMO-, promoter-, terminator,
coding sequence, other element-, construct-specific methods that you used but
that did not yield positive results.
|
|
|
|
|
3.3.2 Importing Screening Data
Import
result file lets you import an Excel file with
screening outcomes to save time entering data.
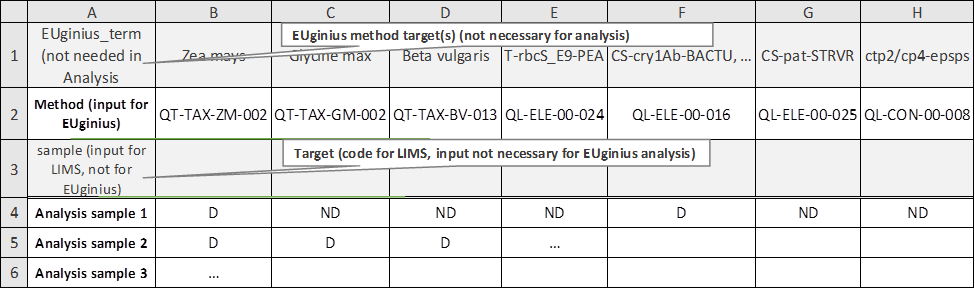
Figure 31 -
Importing screening data for Analysis module
The Excel file which can be imported
(Figure 31) has a layout especially designed for easy entry in either EUginius
or a LIMS (laboratory information management system).
|
Row
1
|
Row 1 is redundant for data analysis purposes; it purely provides
the user of the Excel sheet with a name for the method.
|
|
Row
2
|
EUginius’ method abbreviation. This is required for EUginius’
analysis module. For finding the EUginius method abbreviation that corresponds
to your method(s) (see 4.1.2.1 Which method in EUginius corresponds to
the P-35S method from my laboratory?).
|
|
Row
3
|
LIMS’ method abbreviation. This is required for LIMS’ data
management.
|
|
Rows
4+
|
Each row from 4 onwards is a separate screening. Once the analysis
has been run you can switch between screening results by moving pages.
This allows you to run multiple analyses at the same time.
|
|
|
|
|
Column
A
|
A legend describing the contents of the rows behind them.
|
|
Columns
B+
|
A matrix of screening information showing test results per method
for the different screening samples.
|
|
|
|
|
D
|
Detected, the test showed a positive result.
|
|
ND
|
Not Detected, the test showed no result.
|
|
-
|
Blank, this test was not performed.
|
After clicking the Analyse button, EUginius will begin to calculate which parts of
your screening data coincide with the detected GMOs and which other GMOs may be
present that have not been accounted for in your screening. When you have used
an import file with results, the samples will be shown one by one on separate
pages.
GMO
Information is provided in a matrix with colour
coding and symbols. These colours and symbols have the following meanings:
|

|

|
Unexplained
detected target (detected target not present in any of the identified GMOs)
|
|

|

|
Confirmed
not-detected target (tested but not detected)
|
|

|

|
Explained
detected target (detected target present at least in one of the identified
GMOs)
|
3.3.3.1
Confirmed output
The parameters which EUginius used in the
analysis are displayed first (Targets detected by used methods/ Targets not
detected by used methods).
Then, the analysis report shows the GMOs which
were identified with the event specific method(s) as well as the elements which
were detected. Additionally, it is indicated if the presence of the detected
elements can be explained by the GMOs identified (green underlined) or not (red
underlined).
In the table, complementary information on
the identified GMOs are displayed (Figure
32).
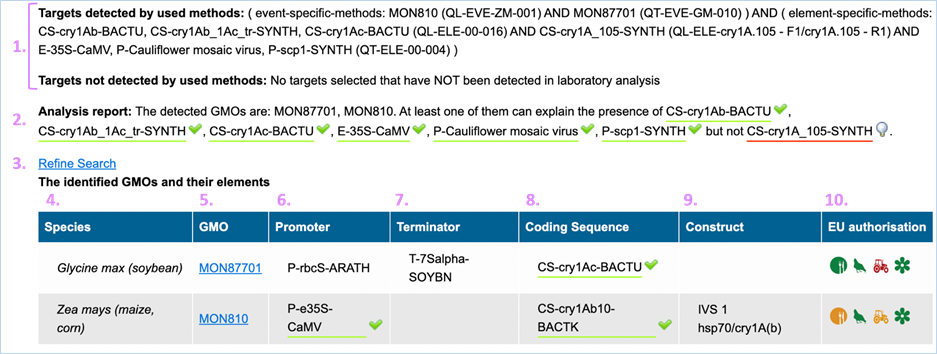
Figure 32 - Confirmed output
|
1.
|
Targets detected by used
method/Targets not detected by used method
|
Parameters which were used in the analysis are listed in this
section.
|
|
2.
|
Analysis Report
|
Lists targets which were detected (GMOs/ constructs/ elements).
This
should match what you entered in step 1 of the module
|
|
3.
|
Refine Search
|
Brings you back to the GMO analysis module
All
entered values should be preserved
|
|
4.
|
Species
|
Species of the GMO
|
|
5.
|
GMO
|
GMOs name
Clicking
the GMO name will lead you to the GMO detailed
information section. For more information on this section consult 3.1.4 GMO Detailed information-
|
|
6.
|
Promoter
|
All Promoters which are present in the GMO
|
|
7.
|
Terminator
|
All Terminators which are present in the GMO
|
|
8.
|
Coding Sequence
|
All Coding Sequences which are present in the GMO
|
|
9.
|
Construct
|
All Constructs which can be detected in the GMO
|
|
10.
|
EU authorisation
|
Approval status of the GMO for food, feed, cultivation and other uses.
Additional information on EU authorisation can be found in Authorisation
tab. For more information on this, consult 3.4
Authorisation
|
3.3.3.2
GMO prediction view
The GMO Prediction views shows GMOs
which may explain targets detected in the
sample but not present in be the GMOs identified (Figure
33).
The GMOs are sorted in alphabetical order of the species by default.
Note: It is your choice to restrict
the outcome. EUginius can only make calculations based on your input.
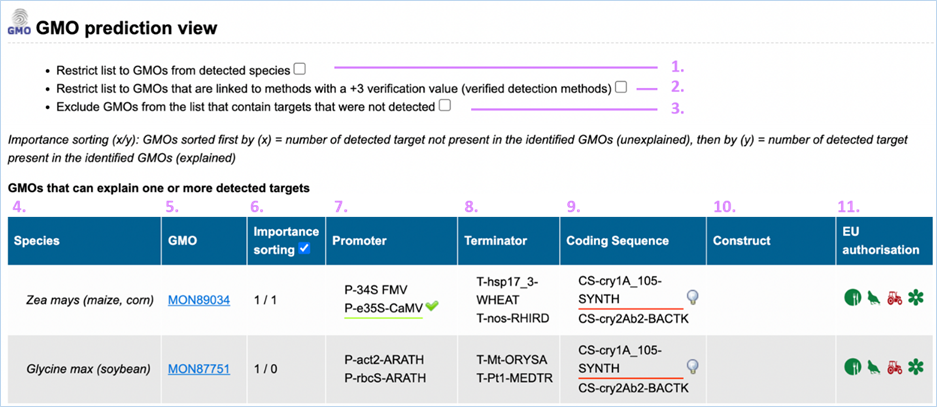
Figure 33 - GMO prediction view (note
that the importance sorting was used in this example)
|
1.
|
Detected Species Only
|
Ticking this box means only GMOs will be shown from species that
you detected.
This
is especially useful if you are sure what kind of material you have.
|
|
2.
|
Verified Methods Only
|
Ticking this box means EUginius will analyse based purely on +3 (practically)
verified methods for GMOs.
Theoretical
matches between method and GMO will not be considered.
|
|
3.
|
Exclude Undetected
|
This will exclude any GMOs that contains target(s) which you
tested for but did not detect.
This
also counts for species.
|
|
4.
|
Species
|
Species of the GMO
|
|
5.
|
GMO
|
GMOs name
Clicking the GMO name will lead you to the GMO detailed information section. For more
information on this section consult 3.1.4 GMO Detailed information
|
|
6.
|
Importance sorting
|
Shows the number of unexplained targets over the amount of
explained targets (in prediction view only).
Checking
the box will put the most likely GMOs on top.
|
|
7.
|
Promoter
|
All Promoters which are present in the GMO
|
|
8.
|
Terminator
|
All Terminators which are present in the GMO
|
|
9.
|
Coding Sequence
|
All Coding Sequences which are present in the GMO
|
|
10.
|
Construct
|
All Constructs which can be detected in the GMO
|
|
11.
|
EU authorisation
|
Approval status of the GMO for food, feed, cultivation and other uses.
Additional
information on EU authorisation can be found in Authorisation
tab. For more information on this, consult 3.4 Authorisation
|
Figure 34 - Authorisation sections
When entering the Authorisation module, you are presented with three different sections:
Search for generic approval, Custom search – EU applications, and Free-text
search (Figure 34).
All sections in this tab provide you with information regarding GMO approval.
3.4.1 Authorisation
Symbols
Many of EUginius’ sections have columns
for EU authorisation. These use coloured symbols to display approval status of the GMO for
food, feed, cultivation and other uses. These symbols indicate the following:
Not Approved
|

|
Food
|
Not
approved for human consumption in the EU
|
|

|
Feed
|
Not
approved for animal consumption in the EU
|
|

|
Cultivation
|
Not
approved for cultivation in the EU
|
|

|
Other
uses
|
Not
approved for any other uses in the EU
|
Approved with Restrictions or Phasing Out
|

|
Food
|
Approved
for human consumption in the EU with restrictions or phasing out
|
|

|
Feed
|
Approved
for animal consumption in the EU with restrictions or phasing out
|
|

|
Cultivation
|
Approved
for cultivation in the EU with restrictions or phasing out
|
|
|
Other
uses
|
Approved
for any other uses in the EU with restrictions or phasing out
|
Approved
|

|
Food
|
Approved
for human consumption in the EU
|
|

|
Feed
|
Approved
for animal consumption in the EU
|
|

|
Cultivation
|
Approved
for cultivation in the EU
|
|

|
Other
uses
|
Approved
for any other uses in the EU
|
Not submitted
|
|
Food
|
Approved
for human consumption in the EU
|
|

|
Feed
|
Approved
for animal consumption in the EU
|
|

|
Cultivation
|
Approved
for cultivation in the EU
|
|

|
Other
uses
|
Approved
for any other uses in the EU
|
|
|
As
of 2023:
MON810 maize is the only GMO with limited approval for EU
cultivation. All other GMOs are not approved for cultivation in the EU.
|
|
3.4.2 Search
for Generic Approval
Search for Generic Approval section lets you find
information on the approval status of a specific GMO for use in food, feed,
cultivation or other uses (Figure 35).
3.4.2.1
Searching
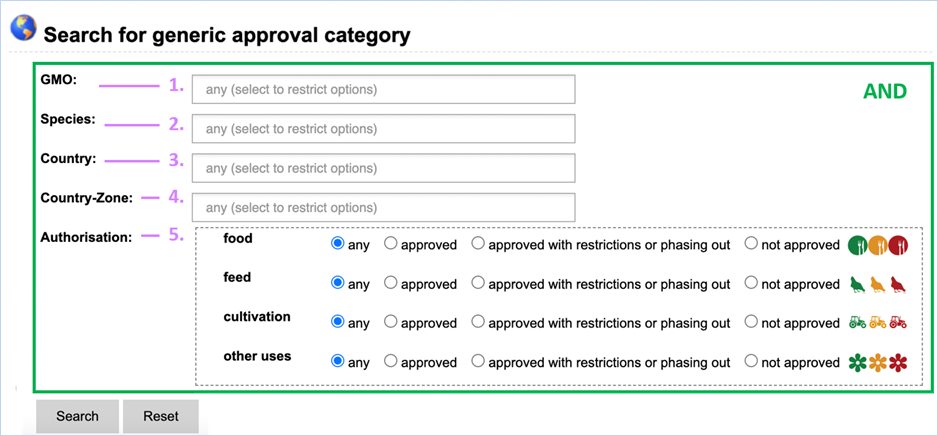
Figure 35 - Search for generic approval
For its searches EUginius makes use of
Boolean operators, specifically AND and OR. All searches in this module use AND
meaning that all provided keywords have to match the search results, narrowing
down the number of results.
Below you can find the meaning of all
keywords that can come up in your searches for generic approval.
|
1.
|
GMO
|
The name(s) of GMOs of which you want to know the authorisation
status.
|
|
2.
|
Species
|
The species for which you want to know the authorisation status.
|
|
3.
|
Country
|
The country/region for which the authorisation applies.
For
regulatory reasons, EU is considered a “country” in EUginius.
|
|
4.
|
Country-Zone
|
A larger region which the authorisation applies for.
e.g. Europe
|
|
5.
|
Authorisation
|
Section that lets you specific your search based on authorisation
status of GMOs.
|

Figure 36 - Generic approval search
results
Changing
your search can be done by clicking Refine Search
at the top of the page (Figure
36).
When clicking the link, you are taken back to the generic approval search page.
All previously entered keywords will be maintained in their fields. You can hit
the reset button to clear these.
Sorting
and Navigating Pages can be done using the arrows,
for an explanation on navigating search results consult 3.5.4
Navigating Search Results.
|
1.
|
GMO
|
The name of the GMOs which the approval is for.
Clicking
the GMO name will take you to GMO details, for more information on this consult
3.1.4 GMO
detailed information
|
|
2.
|
Species
|
The species for which you want to know the authorisation status.
|
|
3.
|
Continent
|
Continent in which the shown authorisation status applies.
|
|
4.
|
Country
|
Country in which the shown authorisation status applies.
This
can also be EU for EFSA decisions
|
|
5.
|
National authorisation
|
Authorisation of the GMO for food, feed, cultivation
and other uses. For regulatory reasons, the EU is seen as one nation.
EUginius uses
symbols to indicate authorisation status, for more information on this consult 3.4.1
Authorisation Symbols
|
|
|
|
|
3.4.3 Custom
Search - EU
applications
Here you can use a set of search
parameters which are specific to EU applications or which describe the specificity
of the GMO(s) subject of EU applications (Figure 37).
The criteria are included when selected
under positive criteria and excluded when selected under negative criteria.
You can expand the list of search
parameters for both, positive and negative criteria, by adding optional
filters. There are seven filters which can be added to or removed from the
selection.
Stacks can be included (default) or excluded
from the search.
3.4.3.1
Searching – positive criteria
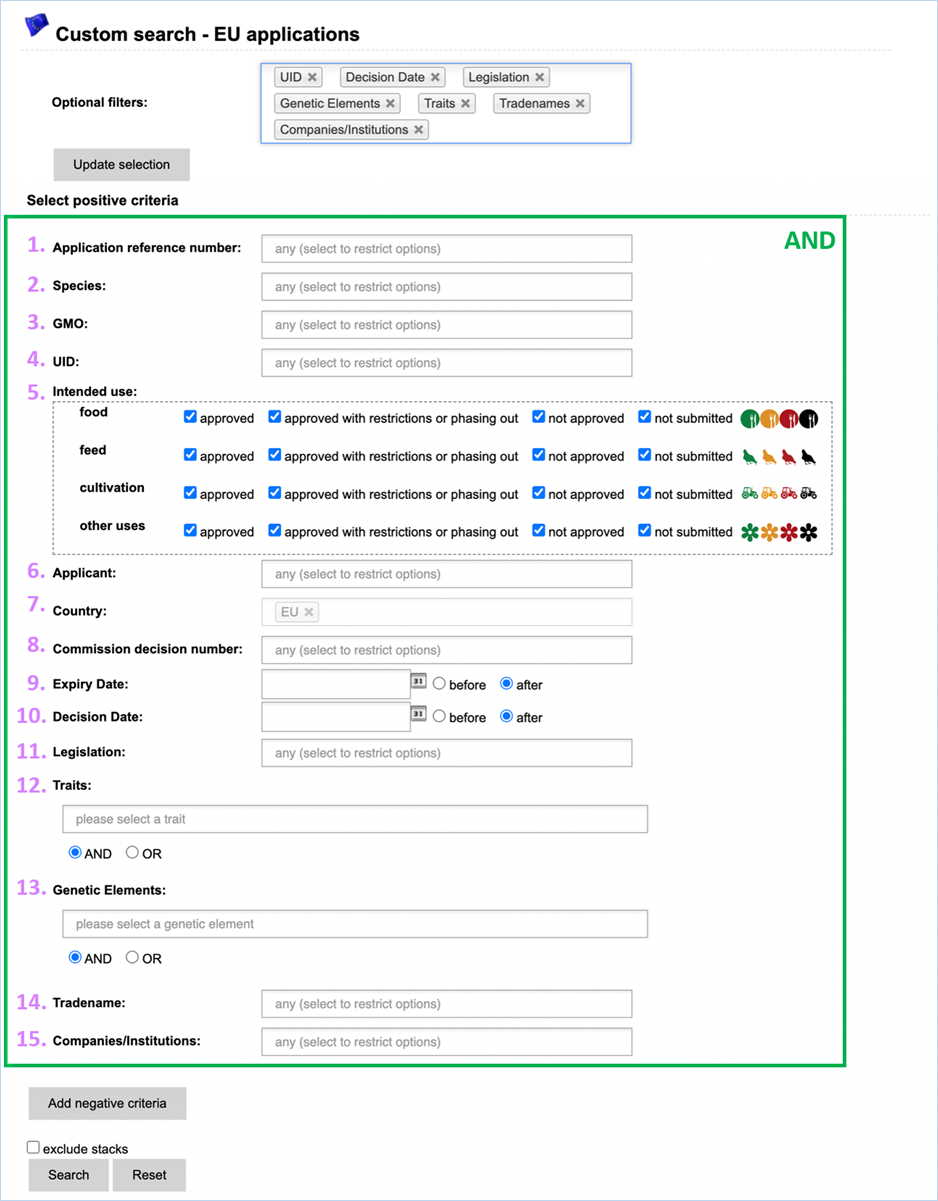
Figure 37 – Explanation custom search
For its searches EUginius makes use of
Boolean operators, specifically AND and OR. All fields are combined in the
query with AND, meaning that all provided keywords have to match the search
results, narrowing down the number of results. Multiple selections in one field
are combined with OR, meaning the result should match one of the keywords in this
field unless you can choose between AND and OR (fields Traits and Genetic
Elements).
Below, you can find the meaning of all
keywords that can be used in the EU applications searches. Numbers in parentheses
correspond to optional criteria.
|
1.
|
Application reference
number
|
A unique identifier for the application, assigned to it by the
institute which received the application.
|
|
2.
|
Species
|
Species for which you want to find information.
|
|
3.
|
GMO
|
Name(s) of GMOs for which you want to find information.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4.)
|
UID
|
Unique Identifier code for GMOs.
|
|
5.
|
Intended use
|
Use(s) and EU authorisation status for the GMO(s).
|
|
6.
|
Applicant
|
The company / institution which submitted the application.
|
|
7.
|
Country
|
Country in which the authorisation applies.
|
|
8.
|
Commission decision number
|
Number of the Commission Implementing Decision.
|
|
9.
|
Expiry date
|
Date on which the authorisation expires.
|
|
(10.)
|
Decision date
|
Date of the European Commission decision.
|
|
(11.)
|
Legislation
|
Legislation under which the application was submitted / the
authorisation is granted
|
|
(12.)
|
Traits
|
Traits which can be exhibited by GMOs
|
|
(13.)
|
Genetic Elements
|
Elements which can be inserted in GMOs
|
|
(14.)
|
Tradenames
|
The name(s) which the GMO is
commonly sold under
|
|
(15.)
|
Companies/Institutions
|
The company/institution which developed
the GMO as well as companies producing or selling the GMO.
|
All values entered here will be considered
in the results.
3.4.3.2
Searching – Negative criteria
Below the section Search for positive criteria
you can select negative criteria (Figure 37), which will exclude search results
from your query. The fields and queries function as within the positive criteria
search (Figure 37).
EUginius
opens up the option to show three result tables, which all can be exported as an Excel file (see section 3.6 Exporting data):
·
All applications: all applications that meet the search criteria (Figure
38a),
·
Valid applications: applications that meet the search criteria and have at least one authorisation
status currently set to approved, approved with restrictions, phasing out or pending,
·
Further applications: applications that meet the search criteria and do
not have any authorisation status set to approved,
approved with restrictions, phasing out or pending.
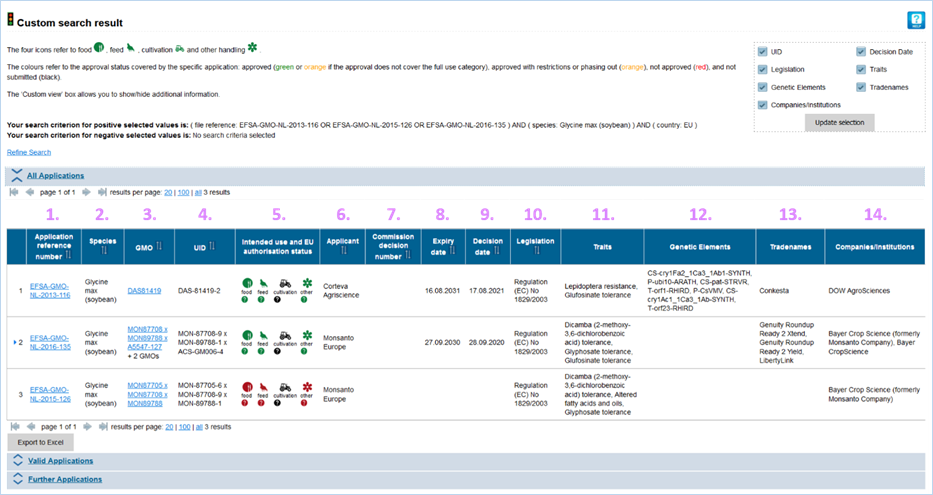
Figure 38a - Custom
search results
Changing
your search can be done by clicking Refine Search
at the top of the page. When clicking the link, you are taken back to the custom
search page. All previously entered keywords will be maintained in their
fields. You can hit the reset button to clear these.
Sorting
and Navigating Pages can be done using the arrows,
for an explanation on navigating search results consult 3.5.4
Navigating Search Results.
|
1.
|
Application reference
number
|
Number from the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) assigned to
the application
|
|
2.
|
Species
|
Species for which you want to find information.
|
|
3.
|
GMO
|
Name(s) of GMOs for which you want to find information.
Clicking
the GMO name will lead you to the GMO Detailed
information section. For more information on this section consult 3.1.4 GMO
Detailed information.
 e.g. “+2 GMOs” indicates that there are two more
GMOs covered by the application. Clicking on the blue arrow symbol ( )
in the first column expands the list with the additional GMOs. e.g. “+2 GMOs” indicates that there are two more
GMOs covered by the application. Clicking on the blue arrow symbol ( )
in the first column expands the list with the additional GMOs.
|
|
(4.)
|
UID
|
Unique Identifier code for GMOs.
|
|
5.
|
Intended use
|
Use(s) and EU authorisation status for the GMO(s).
|
|
6.
|
Applicant
|
The company / institution which submitted the application.
|
|
7.
|
Commission decision number
|
Number of the Commission Implementing Decision.
|
|
8.
|
Expiry date
|
Date on which the authorisation expires.
|
|
9.
|
Decision date
|
Date of the European Commission decision.
|
|
(10.)
|
Legislation
|
Legislation under which the application was submitted / the authorisation
is granted
|
|
(11.)
|
Traits
|
Traits which can be exhibited by GMOs
|
|
(12.)
|
Genetic Elements
|
Elements which can be inserted in GMOs
|
|
(13.)
|
Tradenames
|
The name(s) which the GMO is
commonly sold under
|
|
(14.)
|
Companies/Institutions
|
The company/institute which developed
the GMO as well as companies producing or selling the GMO.
|
 The blue arrow symbol ( ) in the first column indicates that there
are more GMOs covered by the application. When you click on the symbol these
additional GMOs are displayed as well (Figure 38b).
The blue arrow symbol ( ) in the first column indicates that there
are more GMOs covered by the application. When you click on the symbol these
additional GMOs are displayed as well (Figure 38b).
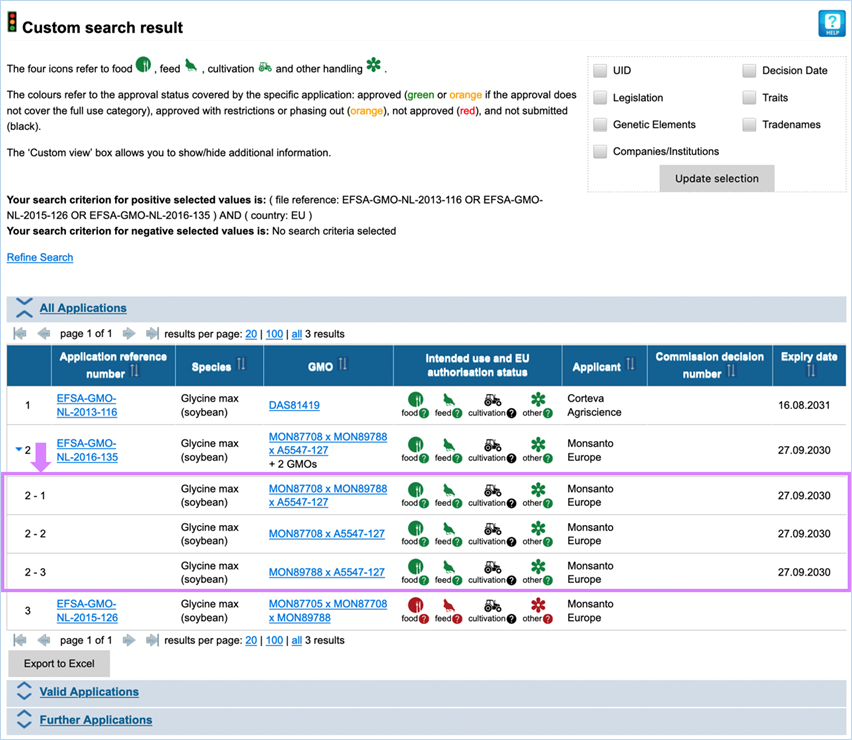
Figure 38b - Custom
search results – expanded GMOs display
3.4.4 Authorisation
Free-text Search
The authorisation free-text search lets
you find all applications submitted in the European Union for authorisation of GMO(s).
It allows the use of application related terms (name of the applicant, the name
of the EFSA application file reference, the Commission Decision Number), as
well as GMO related terms (GMO name, GMO alias, UID, species name (Latin name
or common name), trade name(s), company/institution). The search terms are
highlighted in the result table.
Some examples of free-text searches and
search terms are listed below:
|
Search Term(s)
|
Search result(s)
|
|
*
|
Finds all applications in EUginius
|
|
Bt*
|
names "Bt11", "Bt10 maize",
"BT10 potato", "FR-Bt1", etc.
|
|
305423
|
GMO “DP305423” and its’ UID
"DP-3Ø5423-1"
|
|
Ms8 OR
Rf3
|
GMOs “Ms8” and “Rf3” or stacks with one or both
(e.g. “Ms11 x Rf3” or “Rf3 x GT73”)
|
|
Moon*
|
Tradenames “Moonlite” and “Moonberry”;
additionally, Carnation lines which contain “Moon*” in their Alias – please
note that the latter results are not highlighted in yellow as the GMO alias
is not displayed.
|
|
Gossypium
|
species "Gossypium hirsutum”
|
|
Cotton
|
species " Gossypium hirsutum”
|
|
syngenta
|
Applicant or Companies/Institutions e.g.
"Syngenta Seeds SAS", “Syngenta Crop Protection”
|
|
“Syngenta
Seeds SAS”
|
Specifically finds “Syngenta Seeds SAS”
|
|
EFSA*
|
Finds all Application reference numbers containing
“EFSA”
|
|
“EFSA-GMO-RX-GA21”
|
Specifically finds application “EFSA-GMO-RX-GA21”
|
|
Directive
90/220/EEC
|
All applications submitted under legislation
“Directive 90/220/EEC”
|
|
98/292
OR 2017/1207
|
Applications with the respective Commission
decisions “(EU) 2017/1207” OR “(EC)
98/292”
|
|
98/292 AND
2017/1207
|
No result – no application decided with both Commission
decisions “(EU) 2017/1207” AND “(EC)
98/292”
|
The
display of the result table can be amended using
the box on the right of the page (Figure 39). It allows you to show/hide some
of the columns.
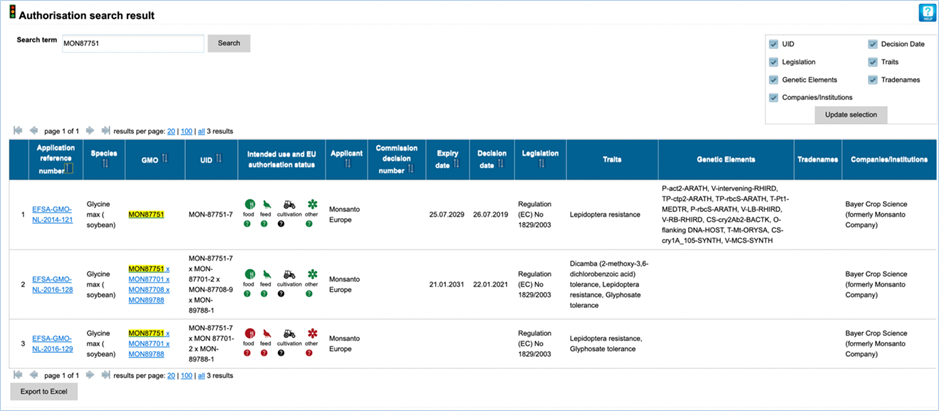
Figure 39 - Results of authorisation
free-text search
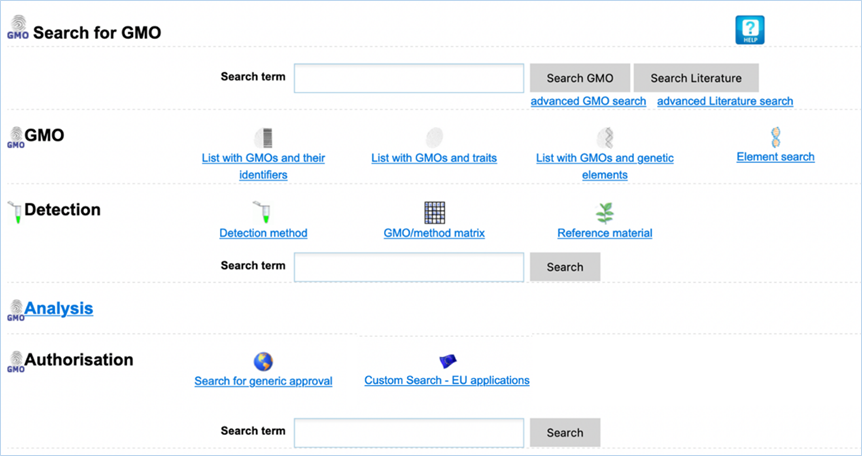
Figure 40 -
Collected search options
In the Search module (Figure 40) you can do a free-text
keyword search on GMOs and literature.
An advanced
search option is also available for GMOs and literature. Clicking the hyperlink
for advanced GMO search will bring you to a
new page, for more information on this consult 3.5.1.1 Advanced GMO Search.
Clicking the
hyperlink for advanced Literature search
will also take you to a new page, for more information on this consult 3.5.2.1
Advanced Literature Search.
Element Search
can only be accessed through this module and it allows you to search for
genetic elements based on GMO, Donor, Species, Elements and Traits. For more
information consult 3.5.3
Element Search.
All other links
and functions from this page can be accessed from outside this module as well.
Information on these other functions and pages was previously discussed in this
manual. The free-text search for detection methods is explained in Chapter 3.2.1.2
Free-text search for methods. The Table of Contents lists all other
chapters and can help you navigate to the specific search functions.
The standard free-text GMO search can find
GMO, UID, Tradename, Species, Company, Traits and Genetic Elements.
Some examples of free-text searches and
search terms are listed below:
|
Search Term(s)
|
Finds GMOs with
|
|
Bt*
|
names
"Bt11", "Bt10 maize", "BT10 potato",
"FR-Bt1", etc.
|
|
305423
|
with UID
"DP-3Ø5423-1"
|
|
MON 00810 6
|
UID
"MON-ØØ81Ø-6"
|
|
RRS
|
alias "RRS" (=GTS
40-3-2)
|
|
zea
|
species
"Zea mays"
|
|
soybean
|
species "Glycine max"
|
|
syngenta
|
UID
"Syngenta"
|
|
yieldgard
|
tradename "YieldGard VT
PRO", "Yieldgard™", "Maxguard/Yieldgard", etc.
|
|
bt11
|
name
"Bt11" and stacks containing Bt11
|
|
insect
|
trait "Insect
resistance"
|
3.5.1.1 Advanced GMO Search
The advanced GMO search (Figure
41) presents
you with seven fields, these correlate to the seven features mentioned above.
The main advantage of the advanced search is filtering out unwanted results, as
it allows exclusion of stacked events and closer specification of search terms.
The advanced search is a query-building search as opposed to a free-text
search. Advanced GMO Search has two
search sections: Select GMOs and Stacks, Search GMOs.
Select
GMOs and Stacks lets you filter for specific GMOs
by picking event-specific GMO names or UIDs.
|
|
Example:
Entering MON810 will show MON810 and all stacks
containing MON810. These results will be the same as a search for MON810’s
UID (MON-ØØ81Ø-6)
|
|
Checking “Exclude stacked events” means
only one GMO shows up per entered keyword, this would be the GMO which you
entered. No stacks of this GMO will be shown in the result list. Exclude
stacked events is selected by default.
Search
GMOs lets you search for GMOs using attributes
instead of names or identifiers.
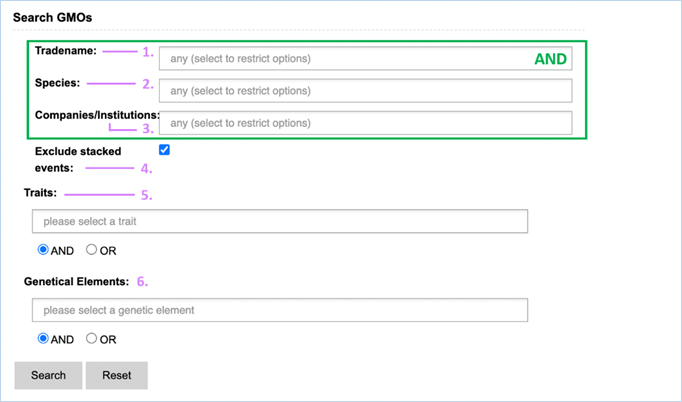
Figure 41 - Advanced GMO search
For its searches
EUginius makes use of Boolean operators, specifically AND and OR. Searching for
traits or genetic elements allows to choose between the two search operators.
|
1.
|
Tradename
|
The name which the GMO is
commonly sold under.
|
|
2.
|
Species
|
Species for which you want to find reference material.
|
|
3.
|
Company
|
Company which produces/sells the GMO.
|
|
4.
|
Exclude stacked events
|
Checking this stops any stacks from being shown.
Stacks are crosses between two different GMOs
|
|
5.
|
Traits
|
Traits which can be exhibited by GMOs.
|
|
6.
|
Genetic Elements
|
Elements which may be integrated/present in GMOs.
|
Search
Results from the advanced GMO search serve the same
function as a filter for the GMO list of identifiers. For any questions
regarding the search results we recommend you consult 3.1.1 List with GMOs and their Identifiers.
The standard free-text literature search
is capable of searching for GMO name, abstract, citation and keywords.
The advanced
literature search presents you with three search options, GMO search,
Genetic Element search and DNA search. Each of these include a name search,
publishing authority specifier and a publication date. Keywords entered in
other sections will not be taken into account when clicking the search button
(see example). The main advantage of the advanced search is filtering out
unwanted results, as it allows for a closer specification of search terms. The
advanced search is a query-building search as opposed to a free-text search.
3.5.2.1 Advanced Literature Search
Advanced GMO Search has three search sections:
GMO search, Genetic Element search and DNA Name search.
|
Searching by
GMO allows for specification of GMO, publishing
authority and publication date.
Useful when you want to know more about a specific GMO
|
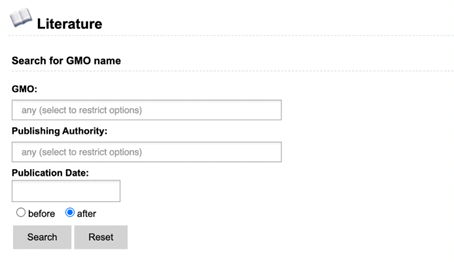
|
|
Searching by
Genetic Element allows for specification of
genetic element, publishing authority and publication date.
|
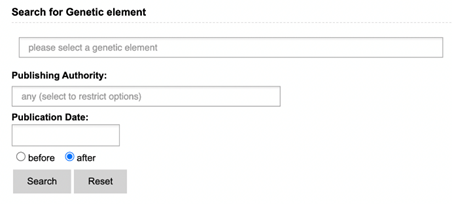
|
|
Searching by
DNA name allows for specification of genetic
element, publishing authority and publication date.
|
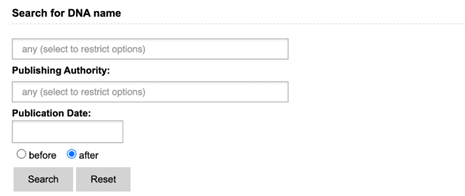
|
|
Publishing authority
usually refers to one specific institution, though “Research Group” can also
be picked here. Picking Research Group
will show any scientific publication matching your criteria.
Publication date may
differ from the application or decision date. Keep this in mind when
searching for literature.
|
3.5.2.2 Literature Search Results
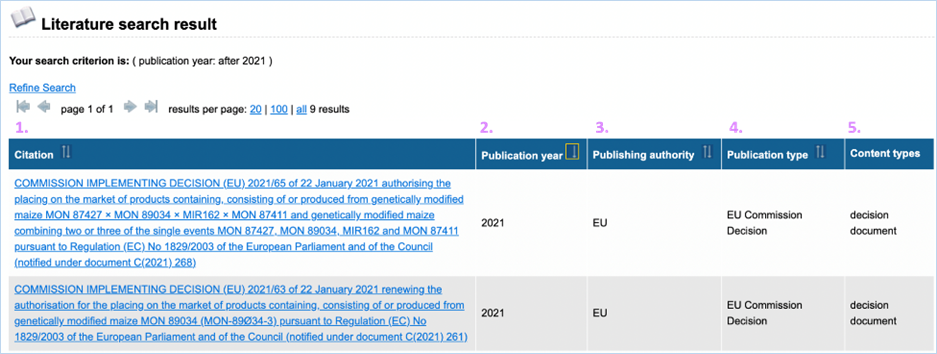
Figure 42 - Literature search results
Changing
Search Criteria can be done by clicking Refine
Search at the top of the page (Figure
42).
When clicking the link, you are taken back to the literature search page. All
previously entered keywords will be maintained in their fields. You can hit the
reset button to clear these.
Sorting
and Navigating Pages can be done using the arrows,
for an explanation on navigating search results consult 3.5.4
Navigating Search Results.
|
1.
|
Citation
|
Literature citation as generally used in references
Research groups publications are
cited in APA 6th edition
Clicking the
citation will lead you to the Literature details section.
For more
information on this section consult 3.5.2.3 GMO Literature
Details
|
|
2.
|
Publication year
|
Year in which the literature was published
|
|
3.
|
Publishing authority
|
Authority which published the literature
|
|
4.
|
Publication type
|
This shows the type of publication and can show you what the
purpose of the publication is.
e.g.
application document, patent, decision or peer-reviewed article
|
|
5.
|
Content types
|
This is a tagging system for EUginius literature with multiple content
types being assigned to literature for different reasons.
e.g.
application, decision, detection, environment, risk assessment and safety
|
3.5.2.3 GMO Literature Details
GMO
literature details gives information about the
literature citation and provides links to the literature. For an explanation of
the module consult Figure 43 and
table below.

Figure 43 - GMO literature details
|
1.
|
Citation
|
Literature citation as generally used in references.
Research
groups publications are cited in APA 6th edition.
Most other documents also stick to a similar standard.
|
|
2.
|
Publication type
|
This shows the type of publication and can show you what the
purpose of the publication is.
e.g. application document,
patent, decision or peer-reviewed article
|
|
3.
|
Comment
|
Notes of the EUginius staff about the literature are added here.
This is generally left empty.
|
|
4.
|
Content type
|
This is a tagging system for EUginius literature with multiple content
types being assigned to literature for different reasons.
e.g.
Application, decision, detection, environment, risk assessment and safety
|
|
5.
|
Keyword
|
Any words which EUginius staff deemed relevant are added here, in
order to aid you in finding the right document.
|
|
6.
|
Publication Year
|
Year in which the literature was published.
|
|
7.
|
Authority
|
Authority which published the literature.
|
|
8.
|
View PDF
|
If available, a .pdf file of the literature can be downloaded here.
|
|
9.
|
View Url
|
A hyperlink to the citation where you can find the text.
Clicking
the hyperlink will open it in a new tab.
|
The Element
Search presents you with six fields that contribute to one query (Figure
44).
This allows specification of GMO, Element Donor, Species and Element or Trait.
With similar fields exclusion of certain
known GMOs, genetic elements or traits is also possible. This helps in the
analysis of detected GMOs when several events are tested for.
3.5.3.1
Element Search
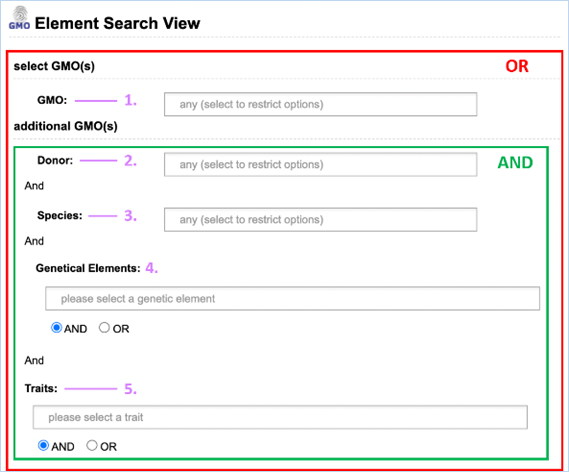
Figure 44 - Explanation of Element
search
For its searches
EUginius makes use of Boolean operators, specifically AND and OR. AND means the result needs to contain all entered
keywords. OR means all GMOs matching the keyword will be shown
regardless of other keywords.
|
1.
|
GMO
|
GMO name
Using this in a search will show all elements inside your
GMO
|
|
2.
|
Donor
|
Species which the genetic element was taken from.
The
element may also be synthetic, this option is also listed
|
|
3.
|
Species
|
Species in which the genetic element has been inserted.
|
|
4.
|
Genetic Elements
|
A query-building search of all elements in EUginius element
thesaurus.
Using
this in a search will show all GMOs and inserts that carry the selected
element
|
|
5.
|
Traits
|
Traits that are attributed to elements in the thesaurus.
|
|
|
Searching
for information on one specific element:
If you have an element’s name and you would like more
information about it, you can type the name in the Genetic Elements
query-building field.
|
|
3.5.3.2
Element Search Results
Figure 45 - Element search results
Changing
your search can be done by clicking Refine Search
at the top of the page (Figure
45).
When clicking the link, you are taken back to the element search page. All
previously entered keywords will be maintained in their fields. You can hit the
reset button to clear these.
Sorting
and Navigating Pages can be done using the arrows,
for an explanation on navigating search results consult 3.5.4
Navigating Search Results.
|
1.
|
GMO
|
GMO wherein the element is found in
Clicking the GMO name will take you
to GMO details, for more information on this consult 3.1.4 GMO detailed
information
|
|
2.
|
Species
|
Species of the GMO
|
|
3.
|
DNA
|
Insert or vector which was used to insert the element into the GMO
Clicking
the DNA name will take you to DNA details, for more information on this consult
3.1.5.1
Genetic Element details
|
|
4.
|
Element
|
The element which matched your search criteria
|
|
5.
|
Donor
|
Species which the
genetic element was taken from
Elements can also be synthetic.
|
|
6.
|
Trait
|
Trait that was introduced into the GMO
This
is only available for coding sequences.
|
3.5.4 Navigating
Search Results

Figure 46 -
Navigating search results
Sorting allows you to arrange your filtered results in alphabetical order
|
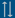
|
Sort
|
The sort symbol
indicates that the feature is not being sorted for
|
|

|
Ascending
|
The ascending
symbol indicates that the feature is currently being sorted for
|
|
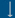
|
Descending
|
The descending
symbol indicates that the feature is currently being sorted for
|
Navigating Pages lets you go through
your results or limit the amount of results you see.
|

|
Next Page
|
Navigate to the
next page
|
|

|
Last Page
|
Navigate to the
last page (e.g. page 25 out of 25)
|
|

|
Previous Page
|
Navigate to the
previous page
|
|

|
First page
|
Navigate to the
first page (page 1)
|
 Several sections
in EUginius allow you to export data using the button.
Several sections
in EUginius allow you to export data using the button.
After clicking this button EUginius will generate
an Excel (.xls) file for you with all information that is presented in the
matrix. All pages are included in the export.
This may take a while depending on the amount of data you want to export. Your
browser will then prompt you with the option to download the exported file.
Exported files adhere to a set format in
EUginius:
Exportpage_YearMonthDay_HourMinuteSecond_Millisecond.xlsx
4.1 Detection: search workflow
for detection methods
4.1.1 Searching for a method
targeting an endogenous maize gene (Taxon-Specific method)
In this example,
we are looking for a taxon-specific method to be used as reference PCR method
for quantification of GM-maize.
We would like to
know:
·
Which methods are available?
·
Which method is suitable to
quantify genetically modified maize?
4.1.1.1
Available maize-specific methods
For this purpose, go to the Detection methods section under the Detection module.
On this page,
there are three different options for a method search. The result tables of
each search contain different type of information.
If we are
searching for maize-specific methods, we can use two of the available search
functions (Figure 47a/ 47b).
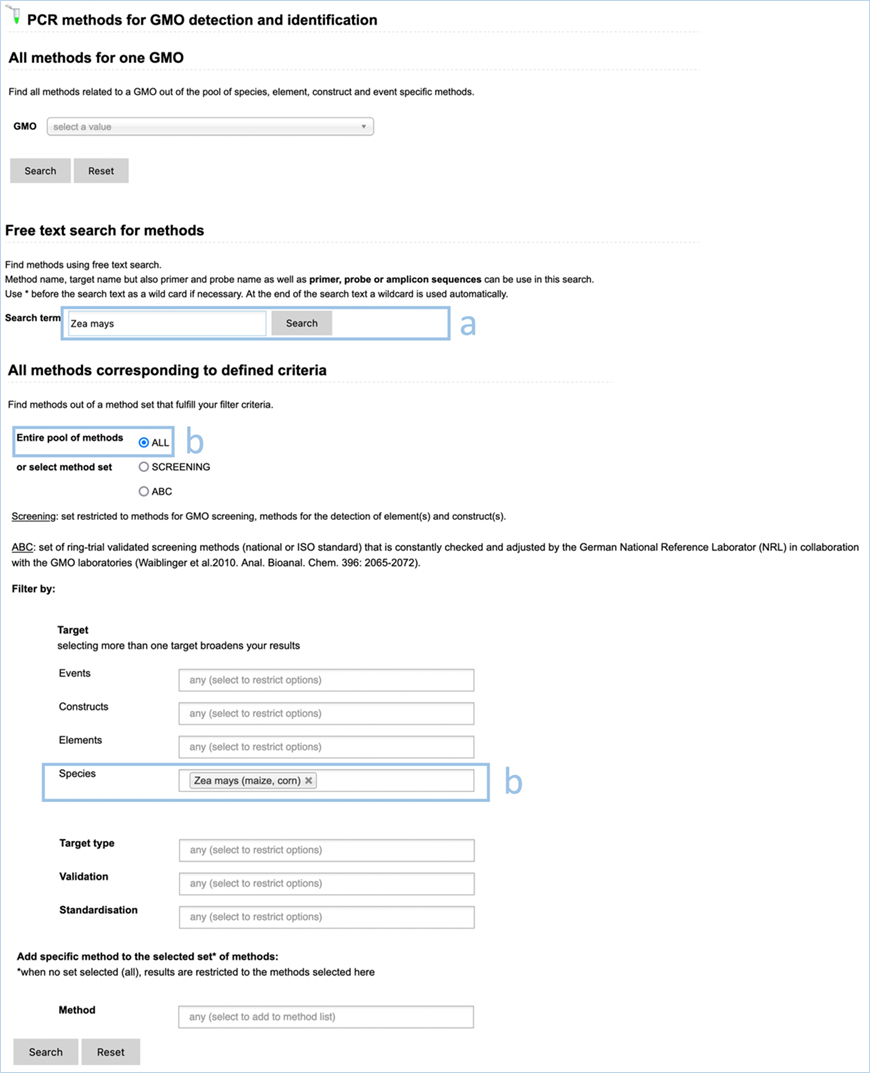
Figure 47 –
PCR methods for GMO detection and identification: Examples a and b show how to
screen for maize-specific methods.
a.
Using the Free text search for methods gives you a result table with technical information.
As the search term enter
the maize Latin name ‘Zea mays’ and
perform the search (Figure 47 (a)).
NB: In this section,
always use the Latin name from species.
You get a list of all the
taxon-specific methods present in EUginius which target a maize specific
sequence. The results table displays the method name (code used in EUginius and
further databases) and all information about the primers/probe and amplicon
sequences (Figure 48).
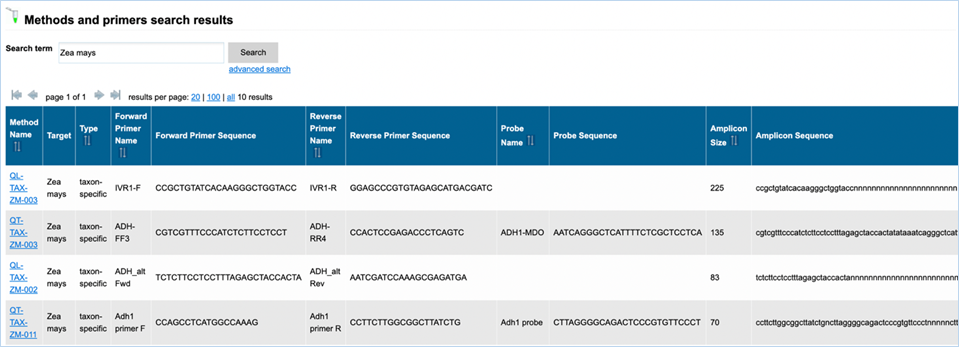
Figure 48 -
Search results – free-text search for maize-specific methods (example a).
There are
currently 10 methods available for the detection of maize.
QT-TAX-ZM-001
and QT-TAX-ZM-014 use the same
primers and probe, QT-TAX-ZM-003 use nearly
the same primer (forward primer has one additional base).
QT-TAX-ZM-002 and QT-TAX-ZM-005 use the same
primers but have different probes.
b.
Using the All methods corresponding to defined criteria search gives you a
result table with qualitative information.
Here you first
indicate if you want to search in a specific set of methods. For our purpose,
we use the entire pool of methods and check ‘All’ (Figure 47 (b)).
Then, you select
suitable filter(s). To look for maize-specific methods, select Zea mays in the filter ’Species‘ and
perform the search (common names are also usable; e.g. maize or corn).
You get a list
with the same maize-specific methods as found previously. However, instead of
the sequence information, the results table displays a short description of the
method with indication of the number of target copies per haploid genome (when
available) as well as information about the type of validation and
standardisation (Figure 49).
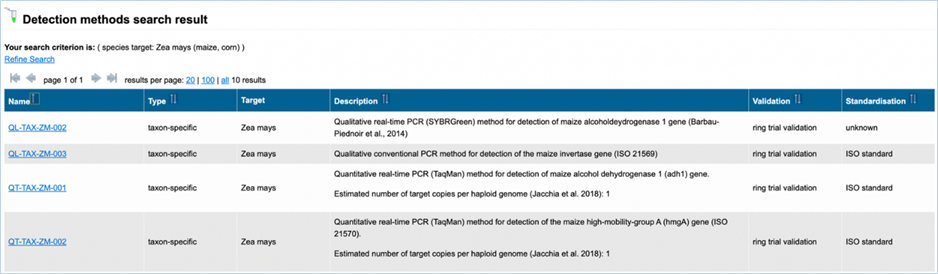
Figure 49:
Search results - All methods corresponding to defined criteria: in this case
all maize-specific methods (example b).
There are
currently 10 methods available for the detection of maize. They were all
validated through a ring trial validation. All but one belongs to the ISO
standard methods or the EU reference method.
Six methods
target the maize alcohol dehydrogenase 1
(adh1) gene and two other methods the
maize high-mobility-group (hmg) gene.
The estimated number of target copies per
haploid genome are indicated for four of the methods, (QT-TAX-ZM-014,
QT-TAX-ZM-004, QT-TAX-ZM-002, QT-TAX-ZM-001).
4.1.1.2
Best method(s) for quantification
analysis of genetically modified maize
When using a taxon-specific method
for quantification purposes, several criteria may be of importance:
·
the validation status of a
method as well as the standardisation give indication on the reliability of the
method
·
the number of target copies per
haploid genome has a direct effect on the calculation.
Therefore, when
looking for a taxon-specific method which should fit for quantification, the All methods corresponding to defined
criteria should be used (see 4.1.1.1.b). In the results
table, (Table 2) you get all necessary information to choose the appropriate
method(s).
Moreover, in
EUginius methods designed for quantification have the prefix QT- (for
quantitative), the methods starting with QL- have been designed for qualitative
analysis.
For maize, the
methods QT-TAX-ZM-001, QT-TAX-ZM-014 are both targeting the single copy gene adh1, both are of high standard
(respectively ISO and EU reference method) and can be used for quantification
purposes. Similarly, the method QT-TAX-ZM-002 which targets the single copy
gene hmgA and belongs to the ISO
standard methods is suitable for quantification.
When using the
QT-TAX-ZM-004 method which targets the maize aldolase (ald1) gene (EU reference method), the two copies of ald1 per haploid genome have to be
considered in the calculation.
EUginius uses a specific syntax for
the naming of the methods (mostly shared with the GMOMETHODS application from
JRC -
https://gmo-crl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/jrcgmomatrix/).
This specific name is used in different tools of the EUginius application (e.g.
GMO/method matrix, analysis tool). It could therefore be useful for the user,
which may have registered the methods with an own naming system, to find the
corresponding method (and official method name) in EUginius.
4.1.2.1
Which method in EUginius corresponds
to the P-35S method from my laboratory?
In EUginius
there are 8 methods registered that target the promoter from the Cauliflower mosaic
virus (P-35S-CaMV; see table below). If
you would like to use the analysis module of EUginius you have to enter the EUginius
method name to select the target detected (or not detected) in your laboratory
analysis. Therefore, finding the correct method name is mandatory.
|
Target
|
EUginius' method name
|
Type
|
|
P-Cauliflower mosaic virus
(P-35S)
|
QL-ELE-00-001
|
element-specific
|
|
P-Cauliflower mosaic virus
(P-35S)
|
QL-ELE-00-004
|
element-specific
|
|
P-Cauliflower mosaic virus
(P-35S)
|
QL-ELE-00-005
|
element-specific
|
|
P-Cauliflower mosaic virus
(P-35S), P-scp1-SYNTH, E-35S-CaMV
|
QL-ELE-00-012
|
element-specific
|
|
P-Cauliflower mosaic virus
(P-35S)
|
QL-ELE-00-017
|
element-specific
|
|
P-Cauliflower mosaic virus
(P-35S)
|
QT-ELE-00-001
|
element-specific
|
|
P-Cauliflower mosaic virus
(P-35S), P-scp1-SYNTH, E-35S-CaMV
|
QT-ELE-00-004
|
element-specific
|
|
P-Cauliflower mosaic virus
(P-35S)
|
QT-ELE-P35S
1-5'
/P35S
1-3'
|
element-specific
|
To check which
one corresponds to the method you use, go to the Detection methods section under the Detection module (Figure 1).
Here, use the Free text search for methods.
·
Use the sequence of one
primer/probe (for example GCCTCTGCCGACAGTGGT; Figure 50), or
·
use the primer/probe name:
EUginius enters the primer/probe name as published in literature.
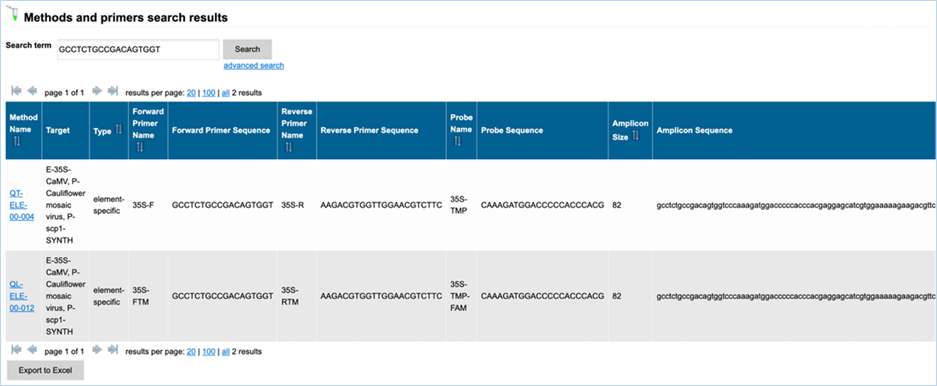
Figure 50:
Search results – in this case the result of a free-text search using a specific
primer sequence.
The search
result (Figure 50) shows that two methods, QT-ELE-00-004 and QL-ELE-00-012, use the specific primer used in the free-text search.
Keep in mind to
check further sequences (reverse primer/probe) to identify/confirm the
corresponding method.
4.2 GMO/method matrix:
Optimisation of a screening strategy
In this example we would like to
know if the pool of screening methods we currently apply allows to detect all
soybean single events authorised in the EU, and whether it provides a good
coverage on non-authorised single events. Finally, we would like to know if
there are methods that we could add to our pool of screening methods in order
to increase the coverage.
Our approach consists
therefore of the following steps:
·
Check the coverage of the
current set of methods – does the set detect all soybean single events
authorised in the EU?
·
Identify events that are not
detected by the methods (screening-gap)
·
Search for methods able to close
the screening-gap
To check the
coverage of the current set of methods, go to the GMO/method matrix section under the Detection tab.
On the left
under Restrict method list by:
select, under ’method’, the methods currently used for the analysis of soybean
(pool of 9 screening methods currently used, see table below):
|
Target
|
EUginius code
|
|
construct: ctp2/cp4-epsps
|
QL-CON-00-008
|
|
construct: P-35S/pat
|
QL-CON-00-011
|
|
element: P-nos-RHIRD
|
QL-ELE-00-008
|
|
element: T-nos-RHIRD
|
QL-ELE-00-011
|
|
element: CS-bar-STRHY
|
QL-ELE-00-014
|
|
element: E-FMV, P-34S FMV
|
QL-ELE-00-015
|
|
element: CS-cry1Ab-BACTU,
CS-cry1Ab_1Ac_tr-SYNTH, CS-cry1Ac-BACTU
|
QL-ELE-00-016
|
|
element:
T-rbcS_E9-PEA
|
QL-ELE-00-024
|
|
element: E-35S-CaMV, P-Cauliflower
mosaic virus
|
QT-ELE-00-004
|
Select on the right under Select GMOs for the GMO/method matrix
the species of interest:
Glycine max
(soybean)
Select all
authorisation status (selected by default) and perform a search (Figure 51).
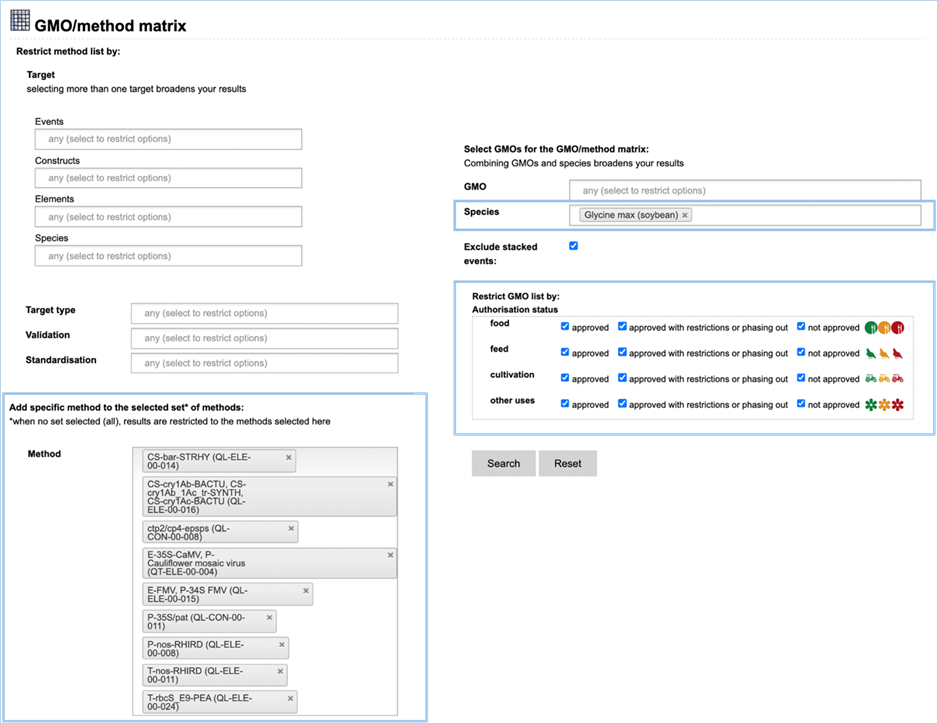
Figure 51–
Example workflow to check the coverage of 9 screening methods to detect all
soybean single event
GMO/method matrix search result gives us matrices assigning verification values to the combinations
of GMOs and detection methods, displayed are:
·
under the banner GMOs detected by selected methods the
GMOs that are detected by at least one of the selected methods (first matrix),
·
under the banner GMOs not detected by selected methods
the GMOs that do not contain any of the target of the selected methods; they
constitute our screening-gap (second matrix).
. 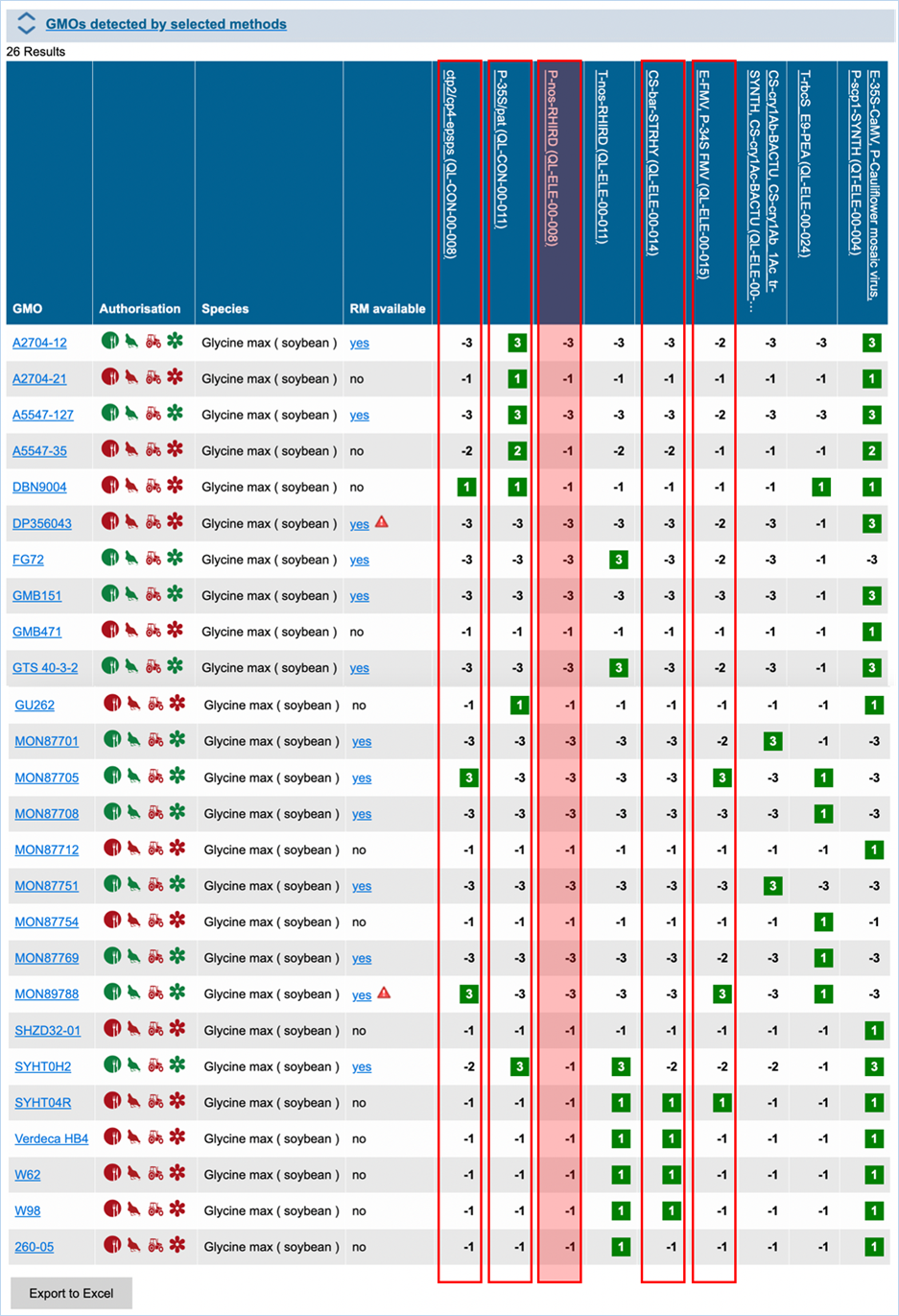
Figure 52 –
Result matrix with 26 soybean events detected by the selected methods.
For an
explanation of this matrix consult 3.2.2.3 Navigating the matrix.
The first matrix
indicates that 26 soybean events are detected by the selected methods (Figure 52).
Moreover, the matrix allows to identify if there are redundancies in our
current strategy (methods that detected events already covered/detected by
other methods).
NB: Methods that
detected only a part of events already detected by another method do not
enlarge the coverage; they can, in some cases, help by the identification of
the events.
In this example,
one method is not adapted to the screening of soybean events (indicated by the
red background), and four methods do not enlarge the coverage (indicated by the
red frame).
The use of a pool reduced to four methods
(T-nos-RHIRD (QL-ELE-00-011), CS-cry1Ab-BACTU,
CS-cry1Ab_1Ac_tr-SYNTH, CS-cry1Ac-BACTU (QL-ELE-00-016), CS-pat-STRVR
(QL-ELE-00-025), E-35S-CaMV, P-Cauliflower mosaic virus (QT-ELE-00-004)) would
allow to detect the 26 events currently depicted.
The second
matrix (‘GMOs not detected by selected methods’) indicates that 9 single events
are not detected by the selected method (Figure 53).
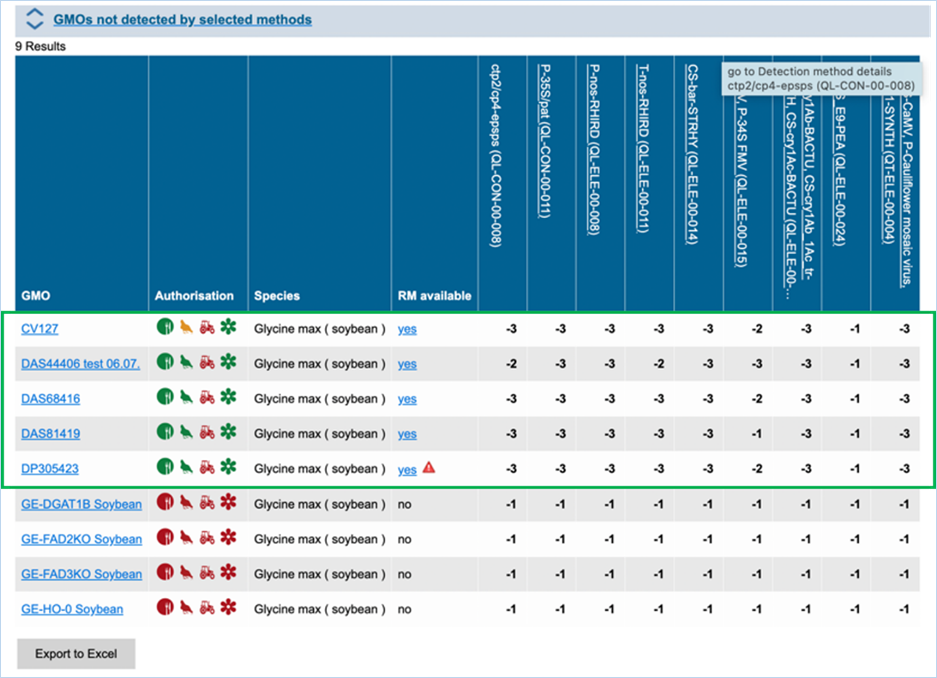
Figure 53 –
Result matrix showing GMOs which were not detected by the search query using
selected methods.
Four out of nine events are genome
edited GMOs (recognisable through the prefix GE in their names). For this type
of GMOs, no screening based on element or construct specific method is
applicable so far. Therefore, those events will not be further considered by
the optimisation of the screening strategy; we will concentrate on the five remaining
GMOs (indicated by the green frame).
To identify
methods that could allow us to detect more of the soybean events, we proceed to
a second search.
For this
purpose, we go to the GMO/method matrix
section using refine search.
We reset the
previous filter parameters.
We select under Select methods for the GMO/method matrix “all”.
We select under Select GMOs for the GMO/method matrix the five
previously identified as not detected GMOs (see green box in Figure 53) and
perform a search.
The
results indicate in the first matrix that the 5 events previously identified as
screening-gap are detected by the selected methods (all), which means that
there is at least one method for each of these events which allows to detect
it.
The
matrix contains all the detection methods present in EUginius (258 as of July
2021) and is therefore very wide. Only details with positive values are
displayed here. Taxon-specific methods are not relevant for our screening
purpose and will not be considered.
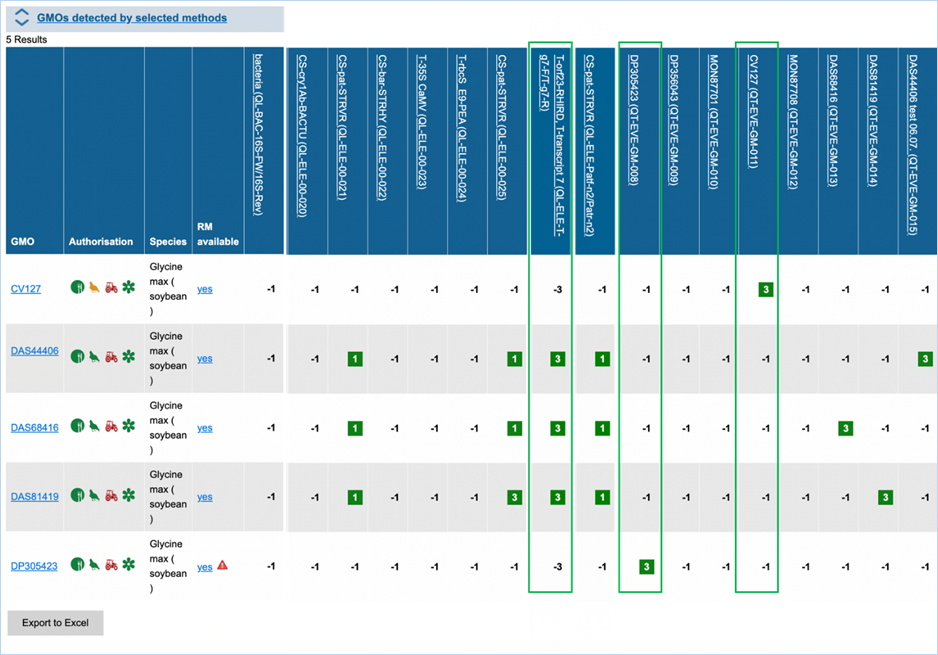
Figure 54 –
Methods with positive values (indicating possibility to detect these GMOs with
the respective method).
Three methods
can be used to close screening-gap (green boxes). Three of the events are
detected by four element-specific methods targeting two different elements.
These events get a verification value of +3 with one of these methods
(targeting both T-orf23-RHIRD and T-transcript 7 (QL-ELE-T-g7-F/T-g7-R)), which
means that the detection of the events has been experimentally verified. This
method would be preferred to complete our screening strategy.
Two events are detected only by their
event-specific methods (DP305423 (QT-EVE-GM-008) and CV127 (QT-EVE-GM-011)). In
order not to miss these events in the screening, these two methods should be
added to the previously mentioned method.
Using the
GMO/method matrix we were able to check our screening strategy. In the first
step we identified four methods that are not necessary for the strict detection
of soybean events. In a second step we were able to find three additional
methods to complete our strategy and close the screening gap.
With a pool of 7
methods, we would be able to detect 31 soybean events including the 16 events
that are authorised in the EU.
4.3 GMO/method
matrix: Designing a Screening strategy
In this example we would like to design a
screening test which allows to detect, on the basis of the elements they
contain, at least the following GMOs:
·
Bt11
·
DAS59122
·
DAS40278
·
GA21
·
MIR162
·
MIR604
·
MON87427
·
NK603
For this purpose,
we go to the GMO/method matrix
section under the Detection tab. Here,
we set the method set to SCREENING and enter the GMOs we would like to detect
(Figure 55).
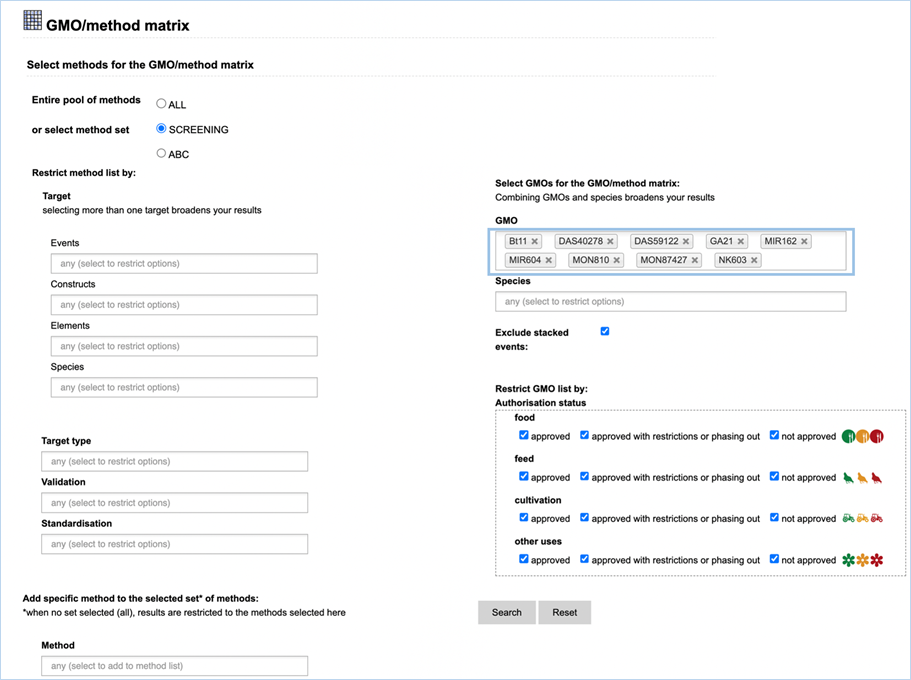
Figure 55 –
Example of a screening for methods to detect specific GMOs in the GMO/method matrix module.
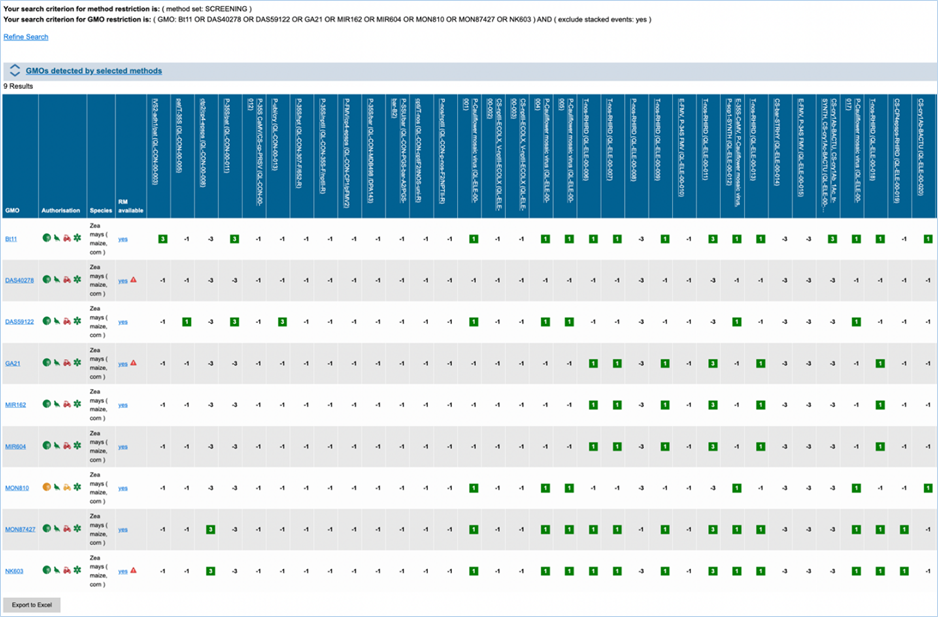
Figure 56 –
GMO/method matrix search result. Note that this is only a part of the matrix.
GMO/method matrix search result gives us a matrix of GMOs and detection methods showing which
methods can detect which GMOs (Figure 56). For an explanation of this matrix
consult 3.2.2.3
Navigating the matrix.
When designing a screening we want to pick
methods in such a way that all GMOs are detected at least once with as few as
possible methods in the screening. Here method-GMO verifications of category +3
are preferred as they are most reliable.
Zoomed in, we see that several methods
detect six of our nine GMOs and could be utilized. T-nos-RHIRD (QL-ELE-00-011) offers the highest reliability here as
its effectiveness for these GMOs has been confirmed (Figure 57, red box).
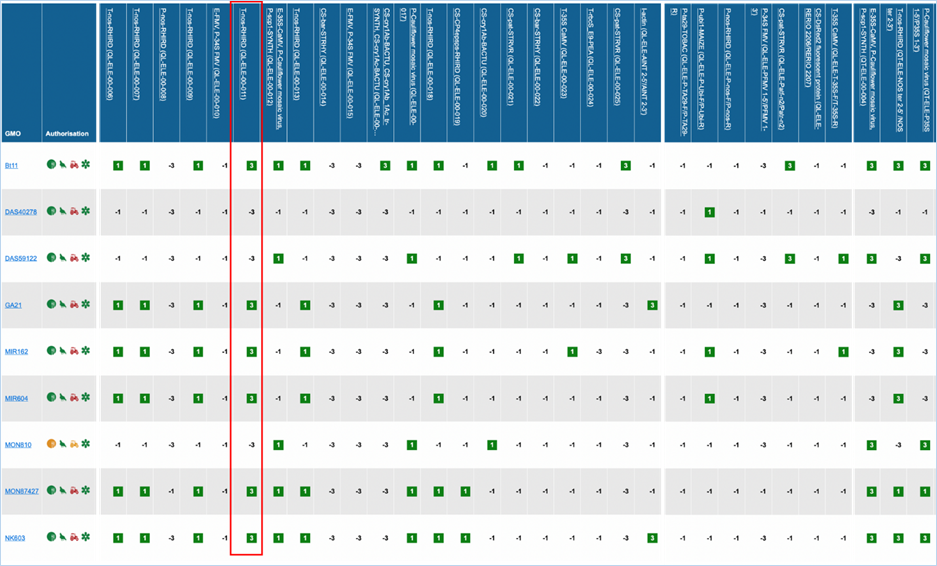
Figure 57 –
The method marked in red (QL-ELE-00-011) offers the highest reliability to
detect 6 out of the selected 9 GMOs.
Now we need to find a method that fills in
most of the gaps. The more additional GMOs are detected here the better. Having
two matches will make identification easier. Several GMOs have a total of five
matches and fill two of the three gaps. Here E-35S-CaMV, P-35S CaMV (QT-ELE-00-004) has the highest reliability
to detect MON810 and DAS59122 (Figure 58, red box).
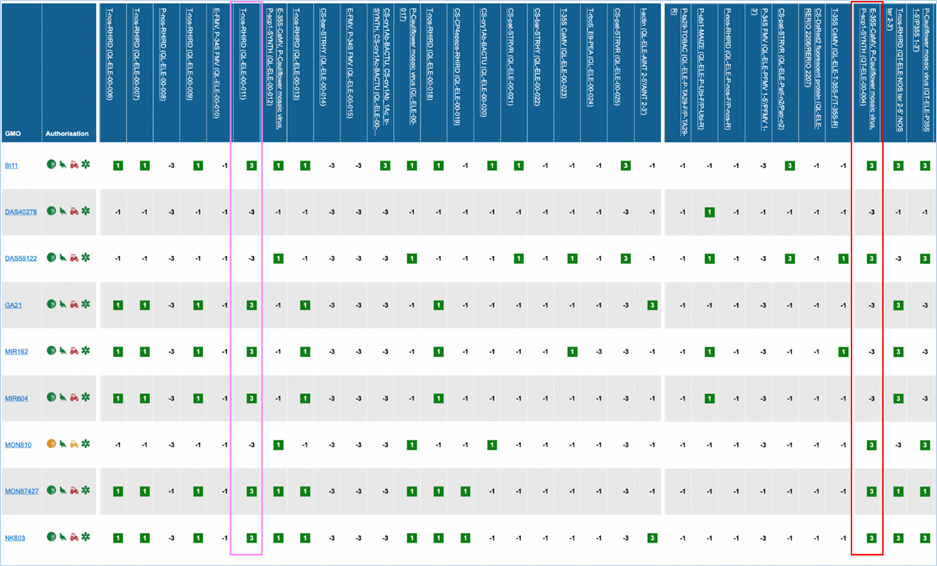
Figure 58 – An
additional method (QT-ELE-00-004) marked in red can be used to detect two of
the three remaining GMOs (MON810 and DAS59122).
After this, there is only one GMO that our screening cannot detect
yet (DAS40278). There is only one method listed that can detect DAS40278 (P-ubi1-MAIZE
(QL-ELE-P-Ubi-F/P-Ubi-R); Figure 59, red box), which we will also
add to the screening.
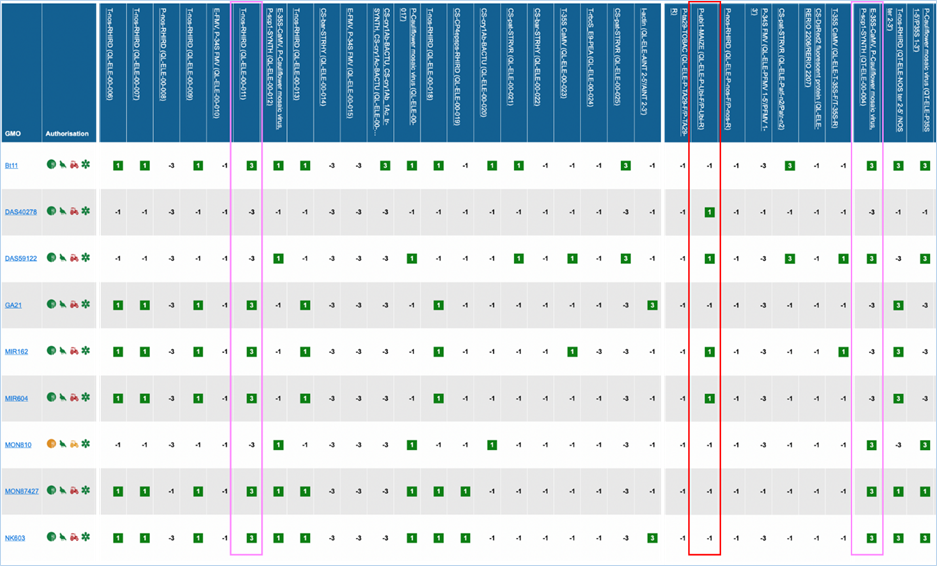
Figure 59 – A
third method (QL-ELE-P-Ubi-F/P-Ubi-R) marked in red fills the last gap to
detect the remaining GMO (DAS40278).
Using EUginius’ GMO/Method
matrix function we determined the optimal screening test for Bt11, DAS59122,
DAS40278, GA21, MIR162, MIR604, MON87427 and NK603. This is composed of:
· T-nos-RHIRD (QL-ELE-00-011)
·
E-35S-CaMV, P-35S CaMV
(QT-ELE-00-004)
·
DAS40278 (P-ubi1-MAIZE
(QL-ELE-P-Ubi-F/P-Ubi-R))
In this example we are given a feed sample
of Zea mays which is presumed to contain
the genetically modified maize event MON810.
We would like to
know:
·
Are there other species in the
sample?
·
Is MON810 really present in
this sample?
o
Which detected elements can be
explained by its presence?
·
Are there elements detected
that are not explained?
·
Which GMOs can explain the
detected elements not present in the identified GMOs?
o
Are these GMOs authorised in
the EU?
o
How do we detect these GMOs?
·
What can we conclude?
In this example, we analysed the feed
sample XD2210-1 with a set of five taxon-, two event-, one construct- and nine element-specific
methods. The results presented in the table below can be entered manually or
with the input file (excel-file containing the table as formatted here, note
that wording of the headers as it is given below is mandatory).
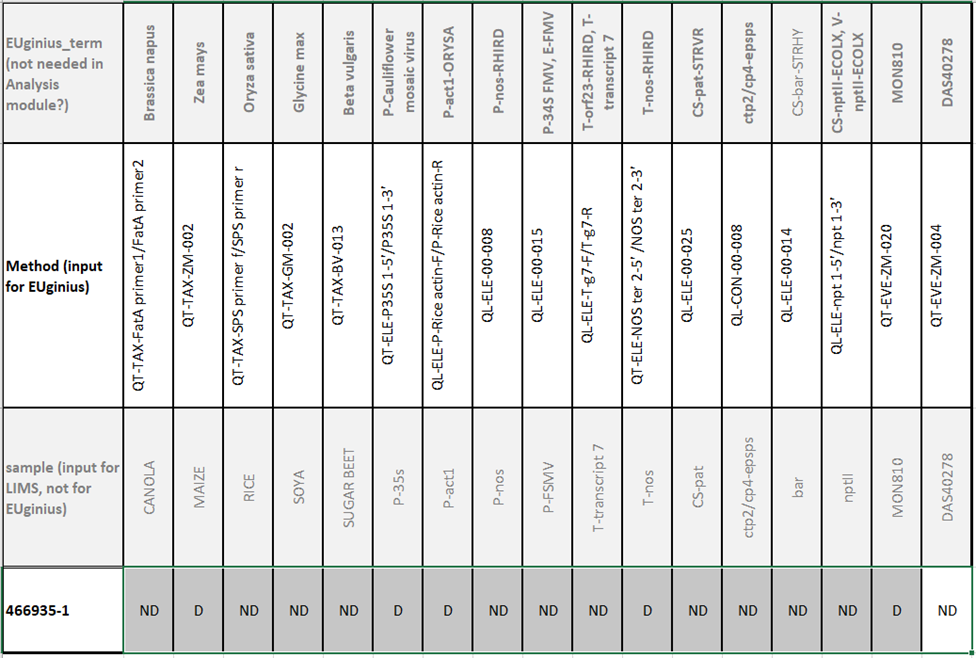
Here we manually inserted the results into EUginius’ analysis module
(Figure 60):
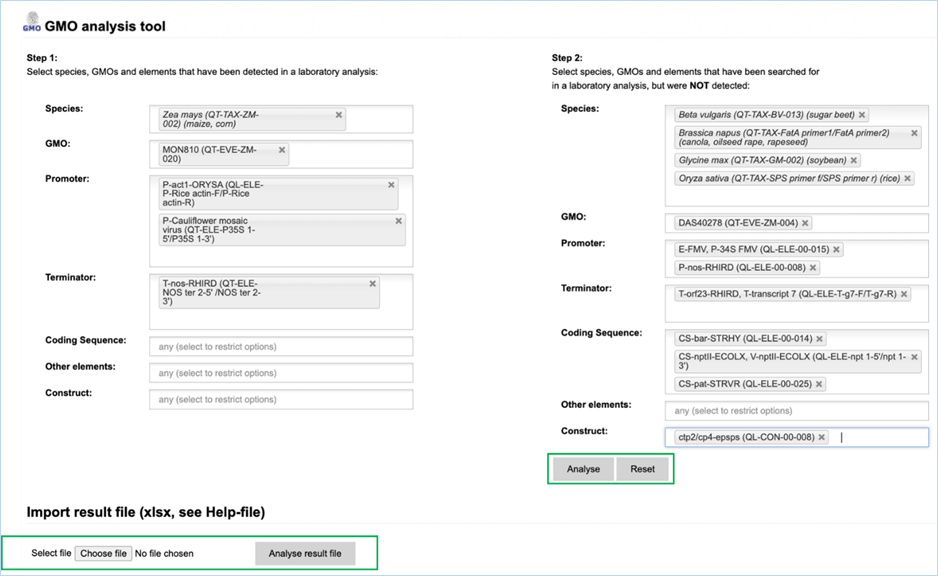
Figure 60 – Example
of a search query in the analysis module. The search parameters can either be
inserted manually or uploaded using an excel-file.
Clicking “Analyse”
makes EUginius analyse your entered screening results. For an upload of an
excel file, you would need to use “Choose file” and “Analyse result file”
(Figure 60).
Confirmed output tells us which elements
can be explained by the GMOs that we have detected (Figure 61).
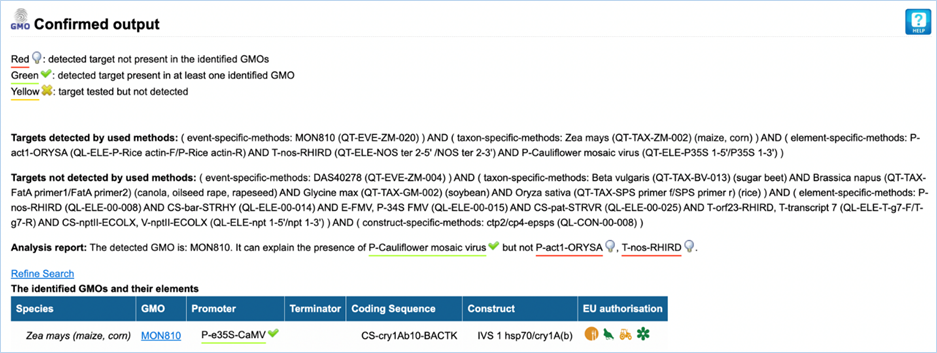
Figure 61 –
Results of the analysis described above. MON810 can explain the presence of the
element P-Cauliflower mosaic virus.
The element P-Cauliflower mosaic virus as
well as all the elements affiliated to it are targets of the selected method
(QT-ELE-P35S 1-5'/P35S 1-3'). In this case, the element P-Cauliflower mosaic
virus can be explained with the presence of MON810 which contains the element
P-e35S-CaMV (affiliated to P-Cauliflower mosaic virus).
Two other elements, P-act1-ORYSA and
T-nos-RHIRD could not be explained by the presence of MON810 in the tested
sample. This means there must be another GMO in the mixture that was not tested
for. The GMO Prediction view can help
us figure out which GMO this might be.
In this case, GMO Prediction View presents us with 170
different GMOs that might be in our sample (Figure 62; note that the numbers of
possible GMOs can vary; the numbers in this example are from August 2021). We
obviously want to reduce the list of possible candidates.
Please realise
that the next steps will reduce the number of likely candidates based on your
own assumptions/expectations.
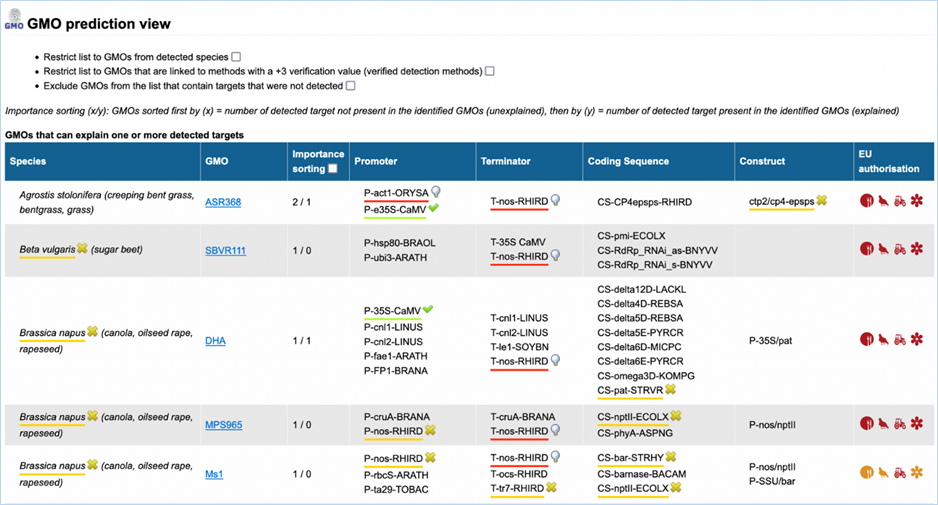
Figure 62 –
GMO prediction view shows all GMOs which might be contained in the analysed
feed sample.
Many of the
listed GMOs come from different species, in this sample however, we do not
expect other species than the five we have tested. Checking the “Restrict list
to GMOs from detected species” box will remove all GMOs from species that we
did not detect (Figure 63). In this case we are only left with Zea mays
GMOs after applying this filter.
After
restricting to detected species we are left with 36 GMOs.
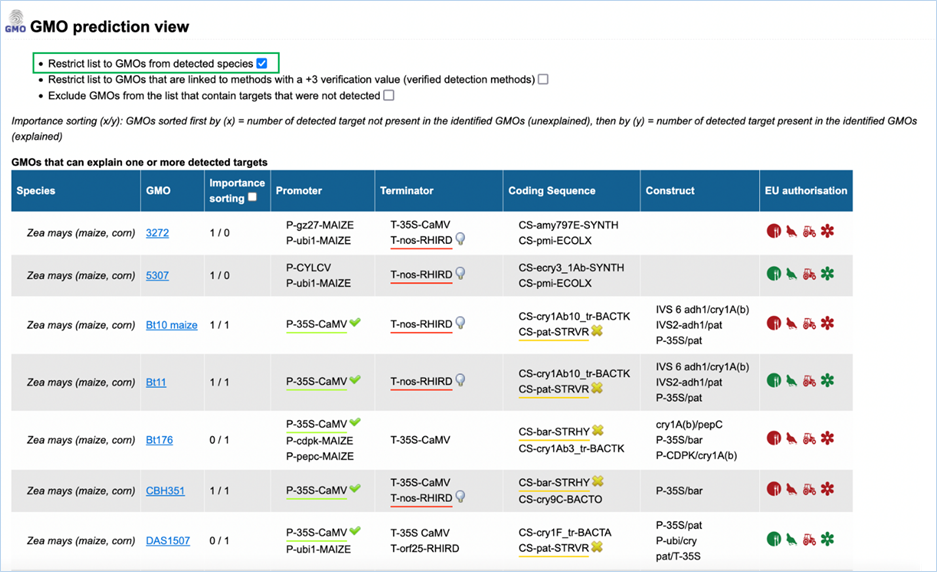
Figure 63 –
GMO prediction view with the restriction to only show species which were part
of the analysis (see green box).
We could test
for the presence of these 36 GMOs, but since we are confident that we correctly
performed our screening, we can eliminate a few more GMOs from this list.
Checking the
“Exclude GMOs from the list that contain targets that could not be detected”
box, will remove all GMOs with elements that we tested for but could not be
detected (Figure 64). These are GMOs with elements that are underlined in
yellow.
After filtering
out not-detected species and not-detected elements, there are 8 GMOs left. One
of them was already identified in the sample (MON810).
By checking
“Importance sorting” we move GMOs to the top that best explain the elements
which were not explained by MON810 (P-act1-ORYSA, T-nos-RHIRD). In this example
GA21 would be the first listed candidate GMO. Here, 2/0 means that:
·
two (2) elements that are not
explained by the presence of the identified GMO (MON810 in this case) are
contained by the GMO listed. Such elements are red underlined.
·
none (0) of the already
explained elements is contained by this GMO. Such an element would be green
underlined.
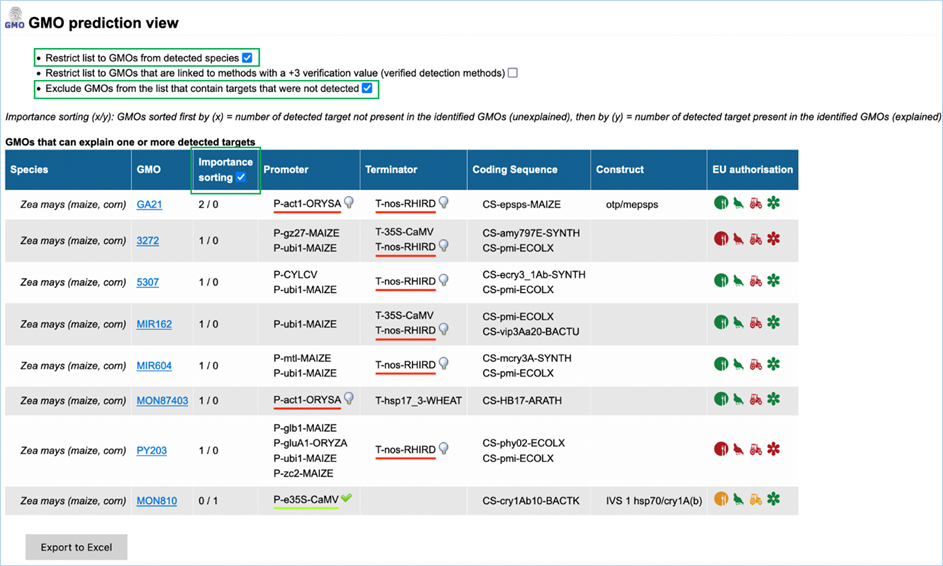
Figure 64 –
GMO prediction view with the restriction to exclude GMOs that contain targets
which were not detected as well as the activated “importance sorting” function.
In this
particular case, events GA21 best explains the unexplained elements as it
contains the two elements which were detected but are not present in MON810. GA21
is authorised for food and feed in the EU.
Six more events
(3272, 5307, MIR162, MIR604, MON87403, PY203) could be in the sample, but would
not suffice to explain all unexplained elements. All but two (3272 and PY203)
are authorised for food and feed in the EU.
In the next
step, we would test for GA21 with an event-specific method.
Clicking the GMO name will take you to
Detection Method GMO Details, which provides you with a list of all detection
methods that will give a positive result for your GMO.
In the case of GA21 we are presented with
22 methods that will show positive for GA21, but not all 22 methods are useful
to us. Since we want a method that is specific to GA21 it should be an
event-specific method. There are two options for GA21: QT-EVE-ZM-007 and
QT-EVE-ZM-014 (the abbreviation -EVE- in the method name indicates an
event-specific method). Both are ring trial validated EU reference methods that
are specific to GA21 and therefore best suitable for our purpose.
In doing this analysis we found out that:
·
Maize is present in the sample.
·
There are none of the other
tested species in the sample.
·
Event MON810 is effectively
present in the sample and can explain the detected target P-Cauliflower mosaic
virus.
·
Most likely, GA21 is in the
sample since it contains both unexplained elements.
·
GA21 can be detected with
QT-EVE-ZM-007 and QT-EVE-ZM-014.
·
Further events could be present
in the sample, but none of them is able to explain alone the unexplained
elements.
·
MON810 is approved for animal
feed in the EU, as is GA21. When GA21 would explain the presence of P-act1 and
T-nos and the sample is marketed as being GMO, it is compliant.
You need to decide if the confirmation of
the presence of GA21 is sufficient for your laboratory, or if you want to
confirm all possible candidates.
On its homepage EUginius offers two links
that allow you to give feedback or to provide input on interesting GMOs.
|
|
Clicking Suggest
new GMO opens your local e-mailing software (e.g. Microsoft Office
Outlook) with numerous filled-in fields. This is the standard layout for
suggesting GMOs (see right).
The To... field should say database@euginius.eu
with Suggested new GMO for EUGINIUS as
subject.
Below this, we
would like you to provide the name of the GMO you would like to see added to
EUginius, your name, e-mail address, your affiliation and a source of
information.
It greatly
benefits EUginius staff if you provide as much information as you have
available.
|
|
|
Clicking Give
feedback opens your local e-mailing software
(e.g. Microsoft Office Outlook) with numerous filled-in fields. This is the
standard layout for giving feedback on EUginius (see right).
The To... field should say databasemanager@euginius.eu
with Feedback on EUGINIUS as
subject.
Below this, we
would like you to provide your name, e-mail address, your affiliation and
your comment/feedback for the EUginius staff.
It greatly
benefits EUginius staff if you provide as much information as you have
available.
|
The most recent
terms of use can be found in EUginius’ footer under
Terms of use.
EUginius is a
web-based database application providing information on genetically modified
organisms. It was jointly developed by the German Federal Office of Consumer
Protection and Food Safety (BVL; Berlin) and the Dutch Wageningen Food Safety
Research (WFSR; Wageningen UR).
EUginius also
consists of an access-restricted section. Access to this section is restricted
to authorised users of institutions that signed a membership agreement.
Permission to use data obtained from EUginius shall be granted subject to the
following terms and conditions:
1.
Authorised users shall receive
a username and password with which they can gain access to the secure/protected
area of EUginius. This user authorisation is personalised and may not be used
by anyone other than the owner.
2.
A written request for access
shall be submitted to BVL through the applicant’s employer.
3.
Authorised users are obliged to
keep their password and username secret in order to avoid risk of abuse by
third parties. If the authorised user becomes aware of any abuse of his/her
access data, he/she shall be obliged to inform BVL without delay.
4.
Authorised users are obliged to
ensure that the contact details they have stored in the EUginius system are
kept up to date at all times. Notwithstanding this, all access authorisations
will be reviewed on a yearly basis.
5.
All data stored in the EUginius
system for which this access authorisation is required shall be used for
official purposes only. Any entry, recording or preservation of the data and
any form of publishing or transfer to third parties is not permitted.
6.
The authorised user shall be
liable for any abuse attributable to him/her. In cases of abuse BVL is entitled
to block that user’s access immediately.
7.
For technical reasons, the
username and its email address will be transferred to servers of the BVL and to
a server of its cooperation partner (WFSR – Wageningen UR) in the Netherlands
for storage once a day during data update. The authorised user hereby agrees to
this.
8.
All data stored in the EUginius
system by authorised users shall be treated confidentially by BVL and by BVL’s
cooperation partner in the Netherlands and shall not be transferred to third
parties.
Data protection
information: Your personal data are processed for access management purposes
and are being stored for ten years. The Controller for personal data processed
is the Federal Office of Consumer Protection and Food Safety, Bundesallee 551,
38116 Braunschweig, Tel: +49 (0)30 18444 99999, email: poststelle@bvl.bund.de. If the conditions
are met, you may – possibly under certain conditions – exercise your rights
according to Art. 7 par. 3, Art. 15 - Art. 18, Art. 20 - Art. 21 and Art. 77 of
the GDPR. You can find further
information here:
https://www.bvl.bund.de/EN/Service/Datenschutz/datenschutz_node.html